Complete Glossary of Health Insurance Terminology
Understanding the definitions for common health insurance expressions and terms will give you a better understanding of how medical insurance works.A B C D E F G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W
To search this Health Glossary, press Ctrl & F and type the word you wish to find into the box.
A . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
AB1672 (California Small Group Law)
What it does: If you are a small employer in California with 2 to 50 employees, an insurer cannot deny you group medical coverage based on the health status of your employees, and premiums can only be slightly higher (+ 10%) than average if employees have health problems. The law´s key provisions are:
- Guaranteed issue and renewal of small group policies,
- Rules on small group rates,
- Limitations on pre-existing condition exclusions, and
- Requirement that plans and brokers provide fair information about all products.
ABN
See Advanced Beneficiary Notice.
Access
A person´s ability to obtain affordable medical care on a timely basis.
Accident
An unforeseen and unintentional act identifiable in time and place.
Accidental Death and Dismemberment (AD&D)
A supplementary benefit rider or endorsement that provides for an amount of money in addition to the basic death benefit of a life insurance policy. This additional amount is payable only if the insured dies or loses any two limbs or the sight of both eyes as the result of an accident. Some AD&D riders pay one half of the benefit amount if the insured loses one limb or the sight in one eye.
Accredited (Accreditation)
A "seal of approval" for health care facilities. Being accredited means that a facility has met certain quality standards. These standards are set by private, nationally recognized groups that check on the quality of care at health care facilities.
ACEP
See Annual Coordinated Election Period.
ACF
Acquisition
The purchase of one organization by another organization.
ACR
See Adjusted Community Rating.
Activities of Daily Living (ADLs)
Most Long Term Care policies use the inability to do a certain number of ADLs (such as 2 of 6) to decide when to pay benefits. Everyday functions and activities individuals usually do without help such as:
- Transferring which shall mean the ability to move into or out of bed, a chair or wheelchair.
- Continence which shall mean the ability to maintain bowel and bladder function; or when unable to maintain bowel or bladder function, the ability to perform associated personal hygiene (including caring for a catheter or colostomy bag).
- Toileting which shall mean getting to and from the toilet, getting on or off the toilet, and performing associated personal hygiene.
- Bathing which shall mean washing oneself by sponge bath or in either a tub or shower, including the act of getting into or out of a tub or shower.
- Dressing which shall mean putting on and taking off all items of clothing and any necessary braces, fasteners or artificial limbs.
- Eating which shall mean feeding oneself by getting food in the body from a receptacle (such as a plate, cup or table) or by feeding tube or intravenously.
Actual Charge
The charge(s) for a particular service/treatment by a health care provider.
Actuary / Actuaries
The insurance professionals who perform the mathematical analysis necessary for setting insurance premium rates.
Acupuncture
An alternative health procedure based on ancient Chinese methods, gaining acceptance in Western hospitals, involving insertion of thin needles at specific pressure points in the body.
Acute Care
Skilled, medically professional care given to a patient in order to restore them to functional health.
Acute Illness
A disease or condition that comes on rapidly and severely, but that with proper treatment, can be cured, such as pneumonia or a broken bone.
Additional Insured
Refers to anyone covered under your health plan that is not named as "insured" in your documentation.
Adjudication
Determination of the amount of payment for a claim.
Adjustments to Income
Such as HSA contributions, these are expenses that directly reduce your total income. Adjustments are considered "above the line" tax deductions and you claim them right on page one of form 1040. There is no need to itemize these deductions in order to claim them as expenses. Adjustments reduce your total income in order to calculate your adjusted gross income.
Adjusted Community Rating (ACR)
A rating method under which a health plan or MCO divides its members into classes or groups based on demographic factors such as geography, family composition, and age, and then charges all members of a class or group the same premium. The plan cannot consider the experience of a class, group, or tier in developing premium rates. Also known as modified community rating or community rating by class.
Administrative Services Only Contract (ASO)
An arrangement in which an employer hires a third party to deliver employee benefit administrative services to the employer. These services typically include health claims processing and billing. The employer bears the risk for health care expenses under an ASO plan.
Admitting Physician
The doctor responsible for admitting you to a hospital or other inpatient health facility.
Admitting Privileges
The right granted to a doctor to admit patients to a particular hospital.
Advance Beneficiary Notice (ABN)
An Advance Beneficiary Notice (ABN) is a written notice from Medicare, given to you before receiving certain items or services, notifying you:
An ABN gives you the opportunity to accept or refuse the items or services and protects you from unexpected financial liability in cases where Medicare denies payment. It also offers you the right to appeal Medicare´s decision. Providers are not required to give you an ABN for services or items Medicare never covers.
- Medicare may deny payment for that specific procedure or treatment.
- You will be personally responsible for full payment if Medicare denies payment.
Advanced Illness
A serious disease or condition that has progressed too far to be cured, such as cancer that has spread throughout the body.
Adverse Selection
A statistical condition within a group when there is a greater demand for medical services and/or more services necessary than the average expected for that group. See Antiselection.
A person who is authorized by an MCO or an insurer to act on its behalf to negotiate, sell, and service managed care contracts. See Broker.
Aggregate
When one or more family member´s covered expenses (combined) meet the annual deductible amount, the annual deductible amount is satisfied for all covered family members.
Aggregate Stop-Loss Coverage
A type of stop-loss insurance that provides benefits when a group´s total claims during a specified period exceed a stated amount.
Allergy Treatment
Treatment of allergy, which may involve allergy testing and physician´s services.
Allowable Charge
The maximum fee that a third party will reimburse a provider for a given service. An allowable charge may not be the same amount as either a reasonable or customary charge.
A disease that affects the motor nerve cells of the spinal cord and causes their degeneration. Patients with this disease can qualify for Medicare coverage regardless of age.
Alternative Medicine
Some medical techniques once considered outside the boundaries of standard practice have become more accepted in recent years and may now be eligible for coverage. Acupuncture, midwives, and osteopathic treatments are examples of formerly excluded treatments that are now covered under many health insurance policies.
Is a place that provides 24-hour-a-day personal care or custodial care to those who suffer from activities of daily living. limitations or cognitive impairment, but who do not need professional nursing or therapy services (such as those offered in skilled nursing facilities and intermediate care facilities). This type of facility may be known as an Assisted Living Facility or a Custodial or Congregate Care Facility.
Alzheimer's Center
A community-based, long-term care program that provides day care for people in the moderate to severe stages of Alzheimer's disease or other related dementias, and provides various resource services for family caregivers and the community at large. Alzheimer's center identify the psychological and social needds of individuals and assist them in functioning at the highest level possible within individual degrees of mental and physical functioning. Also known as an Alzheimer's Day Care Resource Center.
Alzheimer's Disease (Click here for more information)
A progressive, degenerative form of dementia that causes severe intellectual deterioration.
Ambulatory Care
All types of health services that do not require an overnight hospital stay.
Ambulatory Care Facility (ACF)
A medical care center that provides a wide range of Health Care services, including preventive care, acute care, surgery, and outpatient care, in a centralized facility. Also known as a medical clinic or medical center.
Ambulatory Surgery
Surgical procedures performed that do not require an overnight hospital stay.
Ambulette
A wheelchair accessible van that provides non-emergency transportation for people with disabilities. May be owned by the individual or a commercial ambulette service.
Ancillary Services
Auxiliary or supplemental services, such as diagnostic services, home health services, physical therapy, and occupational therapy, used to support diagnosis and treatment of a patient´s condition.
Annual Coordinated Election Period (ACEP)
You can only disenroll or switch plans once per year during the Annual Election Period (AEP) (November 15 - December 31 of each year for benefits that begin the following January).
Annual Deductible
The amount a member pays in any one year for covered services before your health plan starts to pay part of your covered expenses. On many plans, some benefits (such as doctor visits and pharmacy) are not subject to the deductible and are available immediately.
Annual Maximum Benefit Amount
The maximum dollar amount set by an MCO that limits the total amount the plan must pay for all Health Care services provided to a subscriber in a year.
The tendency of persons who present a poorer-than-average risk to apply for, or continue, insurance to a greater extent than do persons with average or better-than-average expectations of loss.Legislation designed to protect commerce from unlawful restraint of trade, price discrimination, price fixing, reduced competition, and monopolies. See also Sherman Antitrust Act, Clayton Act, and Federal Trade Commission Act.
Any Willing Doctor
A doctor, hospital, or other health care provider that agrees to accept the Medicare plan's terms and conditions related to payment and that meets other requirements for coverage.
Any Willing Provider Laws
Legislation that requires health care plans to accept into their PPO and HMO networks any provider willing to agree to the network´s terms and conditions.
Appeal
Request made to a payer to reconsider a decision, such as a claim denial or denied prior authorization request. Most appeals must be submitted in writing within a specified period.
Appropriate Care
A diagnostic or treatment measure whose expected health benefits exceed its expected health risks by a wide enough margin to justify the measure.
Appropriateness Review
An analysis of Health Care services with the goal of reviewing the extent to which necessary care was provided and unnecessary care was avoided.
Approved Charge
The dollar amount on which your insurer bases its payments and your co-payments.
APS
See Attending Physician´s Statement.
Area Agency on Aging (AAA) (Click here for a local agency)
A local (city or county) agency, funded under the federal Older Americans Act, that plans and coordinates various social and health service programs for persons 60 years of age or more. The network of AAA offices consists of more than 600 approved agencies.
ASO Contract
See Administrative Services Only Contract.
Assets
Resources such as savings and checking accounts, stocks, bonds, mutual funds, retirement accounts and real estate.
Assignment
In Original Medicare, this means a doctor or supplier agrees to accept the Medicare approved amount as full payment. If you are in Original Medicare, it can save you money if your doctor accepts assignment. You will still pay your share of the cost of the doctor's visit.
Assignment of Benefits
When an insured person assign benefits, they sign a document allowing the hospital or doctor to collect health insurance benefits directly from the health insurance company. Otherwise, the insured person pays for the treatment and is later reimbursed by the health insurance company.
Assisted Living Facility
A residential living arrangement that provides individualized personal care and health services for people who require assistance with activities of daily living. The types and sizes of facilities vary; they can range from a small home to a large apartment-style complex. They also vary in the levels of care and services that can be provided. Assisted living facilities offer a way to keep a relatively independent lifestyle for people who don't need the level of care provided by nursing homes.
Assistive Devices
Tools that enable individuals with disabilities to perform essential job functions, e.g., telephone headsets, adapted computer keyboards, enhanced computer monitors.
Associate Medical Director
Manager whose duties are often defined as a subset of the overall duties of the medical director.
Associated Group Plans
Fully insured plans issued to employee groups, including those formed by labor unions, nonprofit membership corporations, etc.
At-Risk
Term used to describe a provider organization that bears the insurance risk associated with the Health Care it provides.
Attending Physician´s Statement (APS)
A written statement from a physician who has treated, or is currently treating, a proposed insured or an insured for one or more conditions. The statement provides the insurance company with information relevant to underwriting a risk or settling a claim.
Authorization
The approval of care, for hospitalization, outpatient procedure, certain specialty, etc., by a managed care or insurance company for its member, subscriber, or insured.
Autonomy
An ethical principle which, when applied to managed care, states that managed care organizations and their providers have a duty to respect the right of their members to make decisions about the course of their lives.
B . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W
Balance Billing
Billing a patient for the difference between the dentist´s actual charge and the amount reimbursed under the patient´s dental benefit plan.
Basic Medical Insurance
Insurance covering the typical hospital, surgical, and physician expenses including hospital room and board, cost of x-rays, anesthesia, operating room, additional lab charges, surgeon fees, and routine doctor visits.
Behavioral Health Care
The provision of mental health and substance abuse services.
Beneficence
An ethical principle which, when applied to managed care, states that each member should be treated in a manner that respects his or her own goals and values and that managed care organizations and their providers have a duty to promote the good of the members as a group.
Beneficiary
A person eligible for benefit under a health insurance policy. See Insured.
Benefit
Amount payable by the insurance company to a claimant, assignee, or beneficiary when the insured suffers a loss.
Benefit Cap
Total dollar amount that a payer will reimburse for covered health care services during a specified period, such as one year.
Benefit Consultant
An individual or organization hired by a group planholder to review, analyze, and make recommendations on benefit strategies, including benefit plan design, carrier selection, pricing, etc. An insurance professional who provides information, advice and counseling for their clients.
Benefit Design
The process an MCO uses to determine which benefits or the level of benefits that will be offered to its members, the degree to which members will be expected to share the costs of such benefits, and how a member can access medical care through the health plan.
Benefit Maximum
The most a policy pays for a specified loss or covered service. This can be expressed as either a period of time, a dollar amount, or a percentage of the approved amount.
Benefit Period
The interval during which you will be eligible for benefits. Generally, your benefit period will begin with the first medical service you received for a specific illness and end after you have not been treated for that condition for 60 days.
Berevement Services
Bereavement Services is offered to grieving family members by hospice before, during and for 13 months following the death of the patient. The goal of hospice bereavement care is to enable family members to receive support throughout the grieving process.
Birthing Center
A facility that allows mothers to give birth in a home-like setting.
Blended Rating
For groups with limited recorded claim experience, a method of forecasting a group´s cost of benefits based partly on an MCO´s manual rates and partly on the group´s experience.
Board Certified
A physician who has passed examinations given by a medical specialty group and who has, as a result, been certified as a specialist in this area of practice.
Brand
A name, number, term, sign, symbol, design, or combination of these elements that an organization uses to identify one or more products.
Prescription drug which is marketed with a specific brand name by the company that manufactures it. May cost insured individuals a higher co-pay than generic drugs on some health plans. See Generic.
Bridge (Applies to HSA, HIA+ and PowerHealth Fund plans)
Once health account funds are exhausted, the amount a consumer pays to satisfy their deductible amount - the ‘bridge´ to traditional health coverage, also known as the out-of-pocket responsibility.
A salesperson who has obtained a state license to sell and service contracts of multiple health plans or insurers, and who is ordinarily considered to be an agent of the buyer, not the health plan or insurer. See Agent.
Business Integration
The unification of one or more separate business (nonclinical) functions into a single function.
Affordable Health Insurance Online
C . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W
C&R
Cadillac Health Plans
These are high-cost insurance plans that require little or no out-of-pocket expenses for medical treatment. Many union employees, workers in high-risk professions and corporate executives have them.
Cafeteria Plan (Click here for more information)
A benefit program in which employees are given the ability to choose from a selection ("menu") of benefit plans. Also known as "Flexible Benefits."
Cal-COBRA (Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act)
Cal-COBRA (in California) applies to groups with 2-19 employees (COBRA applies to groups with 20+ employees). Cal-COBRA provides for the continuation of coverage for employees and eligible dependents of qualifying groups with 2-19 employees. Cal-COBRA provides continuation of coverage for groups of 2-19 eligible employees for at least 50% of the working days in the previous calendar year. Groups of one employee are not eligible for Cal-COBRA. An employee and/or his/her eligible dependents are eligible for continuation of coverage under Cal-COBRA for up to 36 months, if coverage was terminated due to any of the following qualifying events:
NOTE: Cal-COBRA rates are 110% of the group rate. See Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act.
- Death of the plan subscriber (continuation for dependents);
- Employee´s termination of employment or reduction in hours;
- Spouse´s divorce or legal separation from the subscriber;
- Loss of eligible dependent status of an enrolled child;
- Subscriber becoming entitled to Medicare;
- Loss of eligible status of enrolled family member.
Calendar Year Deductible
The dollar amount for covered services that must be paid during the calendar year (January 1 – December 31) by members before any benefits are paid by the insurance company. Separate limits are usually applied on a per person and per family basis.
Capital Sum
The amount paid to an insured under an accident or disability policy if the insured suffers the loss of limb, sight or hearing.
Capitation
Capitation represents a fixed monthly dollar amount that a Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) pays to a group of health care providers who have contracted with the HMO. The amount of this fixed dollar amount depends upon the number of HMO enrollees who have chosen this group of health care providers for "primary care" services under the HMO plan. This fixed dollar amount does not vary with how much HMO enrollees use (or don´t use) services offered by this group of HMO providers.
Capped Fee
See Fee Schedule.
Captive Agents
Agents that represent only one health plan or insurer.
Services such as information, advice, and arranging of long-term care by a professional care coordinator.
Care Management Services
A service in which a professional, typically a nurse or social worker, may arrange, monitor, or coordinate long-term care services (also referred to as care coordination services).
Care Plan
A written plan for one´s health care.
Caregiver
A non-specific term describing either a skilled or nonskilled person who provides some type of care for another. In long-term care policies, types of care and types of caregivers are generally defined for purposes of identifying covered services.
Carrier
Insurance company or HMO insuring the health plan. See Third Party.
Case Management
The monitoring and coordination of treatment rendered to patients with specific diagnoses or requiring high cost or extensive services.
Carve-Out
Specialty health service that an MCO obtains for members by contracting with a company that specializes in that service. See also carve-out companies.
Carve-Out Companies
Organizations that have specialized provider networks and are paid on a capitation or other basis for a specific service, such as mental health, chiropractic, and dental. See also carve-out.
Case Management
A process of identifying plan members with special Health Care needs, developing a health-care strategy that meets those needs, and coordinating and monitoring the care, with the ultimate goal of achieving the optimum Health Care outcome in an efficient and cost-effective manner. Also known as large case management (LCM).
Case Manager
A nurse, doctor, or social worker who arranges all services that are needed to give proper health care to a patient or group of patients.
Case-Mix Adjustment
See Risk-Adjustment.
Catastrophic Coverage
Insurance designed to protect you from having to pay high out-of-pocket costs. If you are in good health and simply want to be covered in case of a major illness or accident, then a catastrophic health plan might be the best option for you. Catastrophic health plans usually cover hospital stays, x-rays, and surgical expenses, but do not normally cover mental health care or maternity care.
Catastrophic Coverage Medicare Plan D
Once your total drug costs reach the $7,380.00 maximum (in year 2010), you pay a small coinsurance (like 5%) or a small copayment for covered drug costs until the end of the calendar year.
Catastrophic Illness
A very serious and costly health problem that could be life threatening or cause life-long disability. The cost of medical services alone for this type of serious condition could cause financial hardship.
Catastrophic Limit
The maximum amount of certain covered charges you have to pay out of your pocket during the year. Setting a maximum amount protects you. Separate limits are usually applied on a per person and per family basis.
Catch Up Contributions (HSA) (Click here for more information)
If you are 55 or older and are just starting an HSA, you are allowed to make "catch up" contributions to your account until you enroll in Medicare. In the year you enroll in Medicare, you are required to pro-rate the "catch up" contribution for the number of months you had an HSA qualified high deductible health plan, before the month your Medicare enrollment is effective. Here are the allowable "catch up" contributions:
- 2004: $500
- 2005: $600
- 2006: $700
- 2007: $800
- 2008: $900
- 2009 and after: $1000
Categorically Needy Individuals
Enrollees in Medicaid programs who meet traditional Medicaid age and income requirements.
CCRC
See Continuing Care Retirement Communities.
Center for Medicare and Medicaid (CMS)
Formerly the U.S. Health Care Financing Administration, CMS is an element of the Department of Health and Human Services, which finances and administers the Medicare and Medicaid programs. Among other responsibilities, CMS establishes standards for the operation of nursing facilities that receive funds under the Medicare or Medicaid programs.
Centers of Excellence
Hospitals that specialize in treating particular illnesses, or performing particular treatments, such as cancer or organ transplants.
Certificate Booklet
The plan agreement. A printed description of the benefits and coverage provisions intended to explain the contractual arrangement between the carrier and the insured group or individual. May also be referred to as a policy booklet.
Certificate of Authority (COA)
The license issued by a state to an HMO or insurance company which allows it to conduct business in that state.
Certificate of Coverage
A document given to an insured that describes the benefits, limitations and exclusions of coverage provided by an insurance company.
Certificate of Insurance
This is the printed description of your benefits and coverage limits that forms a contract between you and your carrier. It spells out precisely what will be covered, what won´t, and the dollar maximums.
Certification
CHAMPUS
See Civilian Health and Medical Program of the Uniformed Services.
Chemical Dependency / Substance Abuse
Conditions that include, but are not limited to (1) psychoactive substance induced mental disorders; (2) psychoactive substance use dependence; and (3) psychoactive substance use abuse. Chemical dependency does not include addition to or dependency on, tobacco or food substances (or dependency on items not ingested).
Chemotherapy
Treatment of malignant disease by chemical or biological antineoplastic agents.
Children´s Health Insurance Program (CHIP)
A program, established by the Balanced Budget Act, designed to provide health assistance to uninsured, low-income children either through separate programs or through expanded eligibility under state Medicaid programs.
CHIP
See Children´s Health Insurance Program
Chiropractic Care
An alternative medicine therapy administered by a provider such as a chiropractor, osteopath or physical therapist. The provider adjusts the spine and joints to treat pain and improve general health.
Chronic Condition
Prolonged conditions or illness, such as asthma, diabetes, etc.
Civilian Health and Medical Program of the Uniformed Services (CHAMPUS)
A program of medical benefits available to inactive military personnel and military spouses, dependents, and beneficiaries through the Military Health Services System of the Department of Defense. See also TRICARE.
Claim
An itemized statement of Health Care services and their costs provided by a hospital, physician´s office, or other provider facility. Claims are submitted to the insurer or managed care plan by either the plan member or the provider for payment of the costs incurred.
Claim Form
An application for payment of benefits under a health plan.
Claimant
The person or entity submitting a claim.
Claims Administration
The process of receiving, reviewing, adjudicating, and processing claims.
Claims Analysts
Employees in the claims administration department who consider all the information pertinent to a claim and make decisions about the MCO´s payment of the claim. Also known as claims analysts.
Claims Investigation
The process of obtaining all the information necessary to determine the appropriate amount to pay on a given claim.
Claims Supervisors
Employees in the claims administration department who oversee the work of several claims examiners.
A federal act which forbids certain actions believed to lead to monopolies, including (1) charging different prices to different purchasers of the same product without justifying the price difference and (2) giving a distributor the right to sell a product only if the distributor agrees not to sell competitors´ products. The Clayton Act applies to insurance companies only to the extent that state laws do not regulate such activities. See also Antitrust Laws.
See Consolidated Medical Group.
Clinical Integration
A type of operational integration that enables patients to receive a variety of health services from the same organization or entity, which streamlines administrative processes and increases the potential for the delivery of high-quality Health Care.
A utilization and quality management mechanism designed to aid providers in making decisions about the most appropriate course of treatment for a specific clinical case.
Clinical Status
A type of outcome measure that relates to improvement in biological health status.
Closed Access
A provision which specifies that plan members must obtain medical services only from network providers through a primary care physician to receive benefits.
Closed Formulary
The provision that only those drugs on a preferred list will be covered by a PBM or MCO.
Closed-Panel HMO
An HMO whose physicians are either HMO employees or belong to a group of physicians that contract with the HMO. See Gatekeeper.
Closed PHO
A type of physician-hospital organization that typically limits the number of participating specialists by type of specialty.
Closed Plans
According to the NAIC´s Quality Assessment and Improvement Model Act, managed care plans that require covered persons to use participating providers.
Closed practice
A primary care physician that is not accepting new patients.
CMP
CMS
See Center for Medicare and Medicaid.
COA
COB
COBRA
See Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act.
Coinsurance / Co-Insurance
A method of cost-sharing in a health insurance policy that requires a group member to pay a stated percentage of all remaining eligible medical expenses after the deductible amount has been paid.
Example: If you have a $1,000 deductible with 20% coinsurance and a $10,000 coinsurance limit, this means that after you pay the first $1,000 (deductible) you will then pay 20% of the next $10,000. Meaning you pay twenty cents of every dollar while the insurance company pays the other eighty cents of each dollar ($.20 x 10,000 = $2,000). Once the coinsurance limit is met, the insurance company will pay 100%, giving you an out-of-pocket maximum of $3,000 per calendar year ($1,000 deductible + $2,000 coinsurance).
You will also see the coinsurance written as 80%. You will know what they mean because you will never pay more than 50% coinsurance. You will also see the coinsurance limit written as $2,000. You will know what they mean because coinsurance limits are typically $5,000, $10,000, $15,000 or $20,000, but never more than this. This means your portion (20% in this example) is $1,000, $2,000, $3,000 or $4,000 respectively.Coinsurance Maximum
The total amount of coinsurance that an individual pays each year before the carrier pays 100% of allowable charges for covered services. Coinsurance amounts differ with each contract.
Community Rating
A rating method that sets premiums for financing medical care according to the health plan´s expected costs of providing medical benefits to the community as a whole rather than to any sub-group within the community. Both low-risk and high-risk classes are factored into community rating, which spreads the expected medical care costs across the entire community.
Community Rating by Class (CRC)
The process of determining premium rates in which a managed care organization categorizes its members into classes or groups based on demographic factors, industry characteristics, or experience and charges the same premium to all members of the same class or group. See adjusted community rating (ACR).
Compensation Committee
Committee of the board of directors that sets general compensation guidelines for a managed care plan, sets the CEO´s compensation, and approves and issues stock options.
Competitive Advantage
A factor, such as the ability to demonstrate quality, that helps a managed care organization compete successfully with other MCOs for business.
Competitive Medical Plan (CMP)
A federal designation that allows a health plan to enter into a Medicare risk contract without having to obtain federal qualification as an HMO.
Comprehensive Insurance
A combination of Basic Insurance and Major Medical Insurance.
Concealment
Withholding material facts concerning a risk or a loss. Concealment usually voids coverage.
Concurrent Authorization
Authorization to deliver Health Care service that is generated at the time the service is rendered.
Concurrent Review
Concurrent review involves monitoring the medical treatment and progress toward recovery, once a patient is admitted to a hospital, to assure timely delivery of services and to confirm the necessity of continued inpatient care. This monitoring is under the direction of medical professionals. Concurrent review is a component of "Utilization Review".
Continuing Care Retirement Communities (CCRC)
A Retirement complex that offers a broad range of services and level of care.
Continuation
See COBRA.
Conditionally Renewable
An insurance policy that the company will renew with each premium payment, as long as you meet certain conditions.
Conflict of Interest
For an MCO board member, a conflict between self-interest and the best interests of the plan.
A large single medical practice that operates in one or a few facilities rather than in many independent offices. The single-specialty or multi-specialty practice group may be formed from previously independent practices and is often owned by a parent company or a hospital. Also known as a medical group practice or clinic model.
Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (COBRA)
The Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1985, commonly known as COBRA, requires group health plans with 20 or more employees (in California: 2 to 19 employees for Cal-COBRA) to offer continued health coverage for employees and their dependents for 18 months after the employee leaves the job. Longer durations of continuance are available under certain circumstances. If a former employee opts to continue coverage under COBRA, the former employee must pay the entire premium, usually 110% of the cost of their group coverage.
The plan administrator must notify the employee and the covered spouse of their right to continue coverage within 44 days of the event, except in the case of legal separation or divorce. In those cases, the individual must first notify the plan administrator of the separation or divorce, and the administrator then has 14 days to notify them of their continuation rights. After any of these events, individuals must notify the plan administrator that they want continuation benefits within 60 days after they receive their COBRA or Cal-COBRA notice.
Employees and their dependent spouses and children of these firms who are enrolled in the employer´s employee benefit plans at the time of a qualifying event (defined below) are known as "qualified beneficiaries" and are eligible for COBRA (or Cal-COBRA), unless the individual:
- becomes covered under another group benefit plan which does not impose any pre-existing condition limitations affecting the individual;
- becomes eligible for Cal-COBRA;
- becomes eligible for Medicare;
- becomes eligible for Medi-Cal;
- fails to notify the health plan of a qualifying event in the time specified by the law (generally 60 days); OR
- fails to pay their premium on a timely basis.
Consolidation
A type of merger that occurs when previously separate providers combine to form a new organization with all the original companies being dissolved.
Consumer-Driven Plans
Describes a wide range of approaches to give you more incentive to control the cost of either your health benefits or health care. You have greater freedom in spending health care dollars up to a designated amount, and you receive full coverage for in-network preventive care. In return, you assume significantly higher cost sharing expenses after you have used up the designated amount. The catastrophic limit is usually higher than those common in other plans. Common features include full or partial employee responsibility for several thousand dollars in expenses, and catastrophic coverage covering costs above a certain level, usually higher than those common in other plans.
Continuing Care Retirement Communities (CCRC)
A Retirement complex that offers a broad range of services and level of care.
Contract Management System
An in-formation system that incorporates membership data and reimbursement arrangements, and analyzes transactions according to contract rules. The system may include features such as decision support, modeling and forecasting, cost reporting, and contract compliance tracking.
Contract Year.
The period of time from the effective date of the contract to the expiration date of the contract. A contract year is typically 12 months long, but not necessarily from January 1 through December 31.
Convalescent Home
See Nursing Home.
Conversion Privileges
Group plans generally have a conversion privilege that allows an employee to covert to an individual health insurance plan upon termination of employment. Alternatively, coverage under a COBRA plan may be available.
Coordination of Benefits (COB)
A provision in the contract that applies when a person is covered under more than one health insurance plan. It requires that payment of benefits be coordinated by all plans to eliminate over-insurance or duplication of benefits.
Coordinated Care
Links the treatments or services necessary to obtain an optimum level of medical care required by a patient and provided by appropriate providers. It is also another term for "managed care" used by federal government officials.
Coordination Period
For people with End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) the 30 month period of time during which a group health plan pays first and Medicare pays second. Medicare may pay the remaining costs if your group plan does not pay 100% of your health care bills during the coordination period.
A specified dollar amount that a member must pay out-of-pocket for a specified service at the time the service is rendered.
Corporation
A type of organizational structure that is an artificial entity, invisible, intangible, and existing only in contemplation of the law.
Cost Containment
A set of programs to reduce use of unnecessary or inappropriate services and to encourage provision of necessary and appropriate services in a cost-effective manner.
Cost Sharing
This occurs when the users of a health care plan share in the cost of medical care. Deductibles, coinsurance, and co-payments are examples of cost sharing.
Cost Tiers
See Drug Tiers.
Coverage
Benefits available to an individual covered under a health insurance plan.
Coverage Gap
See Doughnut Hole.
Coverage Restrictions
Restrictions that a health or drug plan may place on certain covered services to restrict their usage.
Covered Benefit
A health service or item that is included in a health plan, and that is partially or fully paid by the health plan.
Covered Charges/Expenses
Most insurance plans, whether they are PPOs or HMOs, do not pay for all services. Some may not pay for prescription drugs. Others may not pay for mental health care. Covered services are those medical procedures for which the insurer agrees to pay. They are listed in the policy.
Covered Dependent
A legal dependent (such as a child) who is covered under the health plan.
Covered Medical Expenses
Charges for medical care provided to an individual while covered under the plan and for which coverage is available under the plan.
Covered Person
An individual who meets eligbility requirements and for whom premium payments are paid for specified benefits of the contractual agreement. See Insured.
Covered Services and Supplies
Usually, the insured will receive a booklet that describes the services and supplies that are covered and reimbursable under the plan. This booklet will probably also describe the types of services and supplies that are not covered and reimbursable under the plan.
CPT
See Current Procedural Terminology.
CRC
See Community Rating by Class.
Credentialing
The process of obtaining, reviewing, and verifying a provider´s credentials the documentation related to licenses, certifications, training, and other qualifications for the purpose of determining whether the provider meets the MCO´s preestablished criteria for participation in the network.
Credentialing Committee
Committee, which may be a subset of the QM committee, that oversees the credentialing process.
Credibility
A measure of the statistical predictability of a group´s experience.
Credit for Prior Coverage
Any previous health insurance coverage that can be used to shorten the pre-existing condition waiting period. See HIPPA.
Critical Access Hospital
A small facility that gives limited outpatient and inpatient hospital services to people in rural areas.
Curative Care
Treatment of patients with the intent of curing their disease or condition; for example...chemotherapy treatments to cure breast cancer.
Cure Provision.
A provider contract clause wich specifies a time period (usually 60--90 days) for a party that breaches the contract to remedy the problem and avoid termination of the contract.
Current Procedural Terminology (CPT)
A system of terminology and coding developed by the American Medical Association (AMA) that is used for describing, coding, and reporting medical services and procedures.
This refers to assistance with daily tasks - such as bathing, eating, or getting in and out of bed. Medicare typically doesn´t pay for custodial care. It is also sometimes referred to as "non-skilled care."
Customary and Reasonable (C&R)
The amount customarily charged for the service by other physicians in the area (often defined as a specific percentile of all charges in the community), and the reasonable cost of services for a given patient after medical review of the case.
D . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W
Day Treatment Center
An outpatient psychiatric facility that is licensed to provide outpatient care and treatment of mental or nervous disorders or substance abuse under the supervision of physicians.
Deductible
Cost-sharing arrangement between an insured person and health insurance company in which the insured person will be required to pay a fixed dollar amount of covered expenses each year before the health insurance company will reimburse for covered health care expenses. Generally, an insured person is responsible for a deductible each calendar year.
Deductible Carry Over Credit
Charges applied to the deductible for services during the last 3 months of a calendar year which may be used to satisfy the following year´s deductible.
Defensive Medicine
Use of unnecessary treatments, procedures or other medical services by doctors to minimize the threat of a malpractice lawsuit.
Demand Management
The use of strategies designed to reduce the overall demand for and use of Health Care services, including any benefit offered by a plan that encourages preventive care, wellness, member self-care, and appropriate utilization of health services.
Denial of Claim
Refusal by a health insurance company to honor a request by an individual (or his or her provider) to pay for health care services obtained from a health care professional.
Dental Care
Under a medical plan, dental care is dental treatment which due to the nature of the procedure or patient´s medical condition, may be provided in a hospital setting.
Dental Health Maintenance Organization (DHMO) (Click for Quote)
An organization that provides dental services through a network of providers to its members in exchange for some form of prepayment.
Dental Insurance
A policy designed to cover pay for your dentist visits and procedures that of not covered by managed care health plans.
Dental Point of Service Option (Dental POS)
A dental service plan that allows a member to use either a DHMO network dentist or to seek care from a dentist not in the HMO network. Members choose in-network care or out-of-network care at the time they make their dental appointment and usually incur higher out-of-pocket costs for out-of-network care.
Dental POS Option
See Dental Point of Service Option.
Dental PPO
See Dental Preferred Provider Organization.
Dental Preferred Provider Organization (Dental PPO) (Click for Quote)
An organization that provides dental care to its members through a network of dentists who offer discounted fees to the plan members.
Dependent
A covered person who relies on another person for support or obtains health coverage through a spouse or parent who is the covered person under a health plan.
Designated Facility
A facility which has an agreement with a health insurance plan to render approved services (Organ transplants are the most common example.). The facility may be outside a covered person´s geographic area.
DHMO
See Dental Health Maintenance Organization.
Diabetes - What is it?
See Health Nation video explanation.
Diagnostic Tests
Tests and procedures ordered by a physician to determine if the patient has a certain condition or disease based upon specific signs or symptoms demonstrated by the patient. Such diagnostic tools include radiology, ultrasound, nuclear medicine, laboratory, pathology services or tests.
Diagnostic and Treatment Codes
Special codes that consist of a brief, specific description of each diagnosis or treatment and a number used to identify each diagnosis and treatment.
Dialysis
The technique used to artifically cleanse yur blood of toxins when your kidneys no longer work either temporarily or permanently.
A planned system of contacts seeking to produce a lead or an order. Using any media, direct marketing requires the use of a database and can be measured in costs and results.
Direct Response Marketing
Disability
The World Health Organization defines Disability as follows: "Disabilities is an umbrella term, covering impairments, activity limitations, and participation restrictions. An impairment is a problem in body function or structure; an activity limitation is a difficulty encountered by an individual in executing a task or action; while a participation restriction is a problem experienced by an individual in involvement in life situations. Thus disability is a complex phenomenon, reflecting an interaction between features of a person’s body and features of the society in which he or she lives.
A type of health insurance coverage that pays you when you are unable to work for an extended period because of an injury or other medical condition. Coverage may be either short-time or long-time.
Discharge
The end of your stay in a medical institution suoch as a hospital or skilled nursing facility.
Discharge Planning
Medical personnel of a health plan working with the attending physician and hospital staff to assess alternatives to hospitalization, evaluate appropriate settings for care, and arrange for the discharge of a patient, including planning for subsequent care at home or in a skilled nursing facility. The goal is to determine when patients are ready to go home, and to provide a more comfortable, cost-efficient setting for continued treatment.
Discount Fees for Service to Providers
HMOs contract with health providers to provide services at discounted rates.
Disease Management Programs (DM)
A coordinated system of preventive, diagnostic, and therapeutic measures intended to provide cost-effective, quality Health Care for a patient population who have or are at risk for a specific chronic illness or medical condition. Also known as disease state management.
Disease State Management
Disenroll
Ending a person´s health care coverage or prescription drug coverage with a health plan or drug plan.
DM
See Disease Management Programs.
DME
See Durable Medical Equipment.
DOB
Date of birth.
Medicare drug plans may have a "coverage gap," which is sometimes called the "donut hole." A coverage gap means that after you and your plan have spent a certain amount of money for covered drugs (no more than $2,830 in year 2010), you have to pay out-of-pocket all costs for your drugs while you are in the "gap." The most you have to pay out-of-pocket in the coverage gap is $4,550. This amount doesn't include your plan's monthly premium that you must continue to pay even while you are in the coverage gap. Once you've reached your plan's out-of-pocket limit, you will have "catastrophic coverage." This means that you only pay a coinsurance amount (like 5% of the drug cost) or a copayment (like $2.50 or $6.30 for each prescription) for the rest of the calendar year.
Drive Time
A measure of geographic accessibility determined by how long members in the plan´s service area have to drive to reach a primary care provider.
A drug approved by the State Department of Health or the Food and Drug Administration and which by law may only be sold with a written prescription of a qualified Health Care provider. Also see Formulary.
Drug Cards
Drug Formulary
A list of preferred pharmaceutical products that health plans, working with an expert panel of pharmacists and physicians, have developed to encourage the dispensing of quality, cost effective medications. Formularies can be classified as:
- Open, in which doctors are encouraged to prescribe medications on the formulary but which allow non-formulary drugs to be covered without prior authorization.
- Restricted, in which only medications on the formulary list are covered.
- Managed, in which doctors are encouraged to prescribe medications on the formulary, but non-formulary drugs are covered with prior authorization.
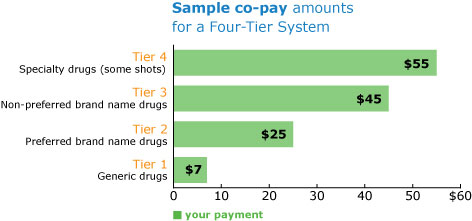
Medications are assigned to one of four (or sometimes five) categories known as copayment or coinsurance tiers, based on drug usage, cost and clinical effectiveness.
- Tier 1 (Generic drugs)
- Generic drugs
- Features the lowest copayment
- Tier 2 (Preferred brand-name drugs)
- Preferred brand-name products based on safety, efficacy, and cost
- Second lowest copayment
- Tier 3 (Brand-name drugs)
- Brand-name drugs for which alternatives are available in Tier 1 or Tier 2; or
- Not used typically as a first line of treatment; or
- Some brand-name drugs with a generic equivalent; or
- Preferred specialty brand-name drugs
- Higher copayment
- Tier 4 (Specialty brand-name drugs)
- Medications classified as those which require special dosing or administration, are typically prescribed by a specialist and are more expensive than most medications
- Highest copayment or coinsurance amount
A review program that evaluates whether drugs are being used safely, effectively, and appropriately.
Due Process Clause
A provider contract provision which gives providers that are terminated with cause the right to appeal the termination.
DUR
Durable Medical Equipment (DME)
Durable Medical Equipment (DME) is considered a Medicare benefit for people needing assistance in a home setting after an illness or accident. The equipment is most often rented and used for a specified length of time. Mechanical devices, equipment and supplies that enable a person to maintain functional ability.
Durable Power of Attorney for Health Care (DPAHC)
A legal document in which a competent person gives another person (called an attorney-in-fact) the power to make health care decisions for him or her if unable to make those decisions. A DPA can include guidelines for the attorney-in-fact to follow in making decisions on behalf of the incompetent person.

E . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W
EAP
See Employee Assistance Programs.
Early and Periodic Screening, Diagnostic, and Treatment Services (EPSDT)
Services, including screening, vision, hearing, and dental services, provided under Medicaid to children under age 21 at intervals which meet recognized standards of medical and dental practices and at other intervals as necessary in order to determine the existence of physical or mental illnesses or conditions. Plans offering Medicaid coverage to EPSDT participants must provide any service that is necessary to treat an illness or condition that is identified by screening.
EDI
See Electronic Data Interchange.
Edits
Criteria that, if unmet, will cause an automated claims processing system to "kick out" a claim for further investigation.
Effective Date
The date health insurance coverage begins.
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
The application-to-application interchange of business data between organizations using a standard data format.
Electronic Medical Record (EMR)
An automated, on-line medical record containing clinical and demographic information about a patient that is available to providers, ancillary service departments, pharmacies, and others involved in patient treatment or care.
Eligibility
Requirements that must be satisfied by people who wish to be insured to establish eligibility.
Eligible Dependent
A dependent of a covered person (spouse, child, or other dependent) who meets all requirements specified in the contract to qualify for coverage and for who premium payment is made.
Eligible Employee
- Full-time employees, employed on a permanent basis with a normal work schedule of at least 30 hours per week, and compensated for that work by the employer (subject to withholding appearing on a W-2 form);
- Part-time employees, employed on a permanent basis with a normal work schedule of either 15-29 hours or 20-29 hours (employer chooses desired option) and compensated for that work by the employer (subject to withholding appearing on a W-2 form). It is the employer´s option to offer coverage to part-time employees; if exercised, employer must offer all similarly situated individuals the same coverage opportunity;
- Sole Proprietors/Partners/Corporate Officers must work at least 20 hours per week to be eligible for coverage;
- Others who may also be eligible subject to underwriting approval include seasonal workers employed by selected agricultural SIC code businesses and private household staff.
Eligible Expenses
The lower of the reasonable and customary charges or the agreed upon health services fee for health services and supplies covered under a health plan.
Elimination Period
The number of days of care that you pay before your insurance plan picks up the benefits.
Embedded Deductible
An embedded deductible would only require a single person on a policy to meet the "individual" deductible, while all members of the family still accumulate toward the maximum family deductible.
Emergency
In general, a sudden, serious, and unexpected acute illness, injury, or condition (including without limitation sudden and unexpected severe pain) which the member reasonably perceives could permanently endanger health if medical treatment is not received immediately. More detailed or slightly different definitions may apply based on applicable law.
Emergency Care
Care for patients with severe or life threatening conditions that require immediate medical attention.
Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs)
Mental health counseling services that are sometimes offered by insurance companies or employers. Typically, individuals or employers do not have to directly pay for services provided through an employee assistance program.
Employee Benefits Consultant
A specialist in employee benefits and insurance who is hired by a group buyer to provide advice on a health plan purchase.
Employee Contributions
Employers are required to pay a minimum amount of each employee´s monthly premium. Employer´s are not required (but have the option) to contribute toward their employees´ dependents´ premiums. Employees pay any remaining premium balance through payroll deductions.
Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA)
A broad-reaching law that establishes the rights of pension plan participants, standards for the investment of pension plan assets, and requirements for the disclosure of plan provisions and funding.
Employer Group Health Plan
Employer Purchasing Coalitions
Employment-Model IDS
An IDS that generally owns or is affiliated with a hospital and establishes or purchases physician practices and retains the physicians as employees.
EMR
See Electronic Medical Record.
End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
A kind of kidney failure. End-stage renal disease requires dialysis or a kidney transplant. Patients with ESRD qualify for Medicare coverage at any age.
Endorsement
See Rider.
Enrollee
The person who is the primary insured. Under an individual or family policy, this person is the applicant. Under an employer-sponsored group health policy, this person is the employee.
Enrollment Period
The period during which individuals may enroll for an insurance policy, Medicare, HMO benefits.
Enterprise Scheduling Systems
Information systems that control the use of facilities and resources for such organizations as physician groups, hospitals, and staff model HMOs.
EOB
Episode of Care
The health care services given during a certain period of time, usually during a hospital stay.
EPO
See Exclusive Provider Organization.
EPSDT Services
See early and periodic screening, diagnostic, and treatment services.
ERISA
See Employee Retirement Income Security Act.
ESRD
Ethics in Patient Referrals Act
A federal act and its amendments, commonly called the Stark laws, which prohibit a physician from referring patients to laboratories, radiology services, diagnostic services, physical therapy services, home health services, pharmacies, occupational therapy services, and suppliers of durable medical equipment in which the physician has a financial interest.
Evidence of Insurability
Proof that you´re in good health.
Evidence of Insurance (EOC)
This contract tells you which benefits and services are covered by the health plan.
Exception Request
A formal, written request to your Medicare drug Part D asking that it pay for a drug you need that is not on its list of covered drugs formulary.
Excess Charges
The difference between a doctor or other health care provider's actual charge and insurance company approved amount for payment.
Exchange
The act of one party giving something of value to another party and receiving something of value in return.
Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO)
An EPO (Exclusive Provider Organization) is a health care benefit arrangement that is similar to a preferred provider organization in administration, structure, and operation, but which does not cover out-of-network care. As a member of an EPO, you can use the doctors and hospitals within the EPO network, but cannot go outside the network for care. There are no out-of-network benefits. An EPO is a type of health plan that utilizes primary care physicians to coordinate access to in-network medical services for plan participants. With the EPO plan, members do not need to select a Primary Care Physician (PCP), and referrals are not needed to access specialty care. Members can access any network doctor or hospital at any time and enjoy the in-network level of benefits. EPOs are structurally similar to PPOs, but EPO members cannot file claims for non-network office visits, which PPO and POS plans allow.
Exclusion Period
A period of time when an insurance company can delay coverage of a pre-existing condition. Sometimes this is called a pre-existing condition waiting period.
Exclusions and Limitations
Medical services that are either not covered or limited in benefit by a health insurance insurance policy.
Exclusive Remedy Doctrine
A rule which states that employees who are injured on the job are entitled to workers´ compensation benefits, but they cannot sue their employers for additional amounts.
Executive Committee
Committee whose purpose is to provide rapid access to decision making and confidential discussions for an MCO board of directors.
Executive Director
In a managed care plan, individual responsible for all operational aspects of the plan. All other officers and key managers report to this person, who in turn reports to the board of directors.
Experience
The actual cost of providing Health Care to a group during a given period of coverage.
Experience Rating
A rating method under which an MCO analyzes a group´s recorded Health Care costs by type and calculates the group´s premium partly or completely according to the group´s experience.
Experimental and Investigational Procedures
Health insurance coverage generally excludes medical treatments that are deemed to be unproven, ineffective, or non-standard. This includes surgical techniques and medicines not approved by the Food and Drug Administration. Sometimes such treatments may be available by traveling to another country, but these treatments would generally not be covered.
Expert System
Software that attempts to replicate the process an expert uses to solve a problem in order to arrive at the same decision that an expert would reach.
Expiration Date
The date coverage expires.
Statement sent by health plans to persons who have experienced a claim under the health plan. The explanation of benefits (EOB) details the charges for the services received, the amount the health insurance company will pay for those services, and the amount the insured person will be responsible for paying.
F . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W
Family Deductible
Deductible that may be satisfied by the combined expenses of all covered family members.
Family Health Insurance
Federal Employee Health Benefits Program (FEHBP)
A voluntary health insurance program administered by the Office of Personnel Management (OPM) for federal employees, retirees, and their dependents and survivors.
Federal Poverty Level (FPL)
The federally set level of income that an individual or family can earn below which it is recognized that they can not afford necessary services. The FPL is used in eligibility criteria of many programs, including Extra Help and Medicaid. The FPL changes every year and varies depending on the number of people in your household.
A federal act which established the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and gave the FTC power to work with the Department of Justice to enforce the Clayton Act. The primary function of the FTC is to regulate unfair competition and deceptive business practices, which are presented broadly in the Act. As a result, the FTC also pursues violators of the Sherman Antitrust Act. See also Antitrust Laws.
Fee allowance
See Fee Schedule.
Fee-for-Service (FFS or PFFS) Payment System
A system in which the insurer will either reimburse the group member or pay the provider directly for each covered medical expense after the expense has been incurred. Also See Private Fee-for-Service Plan (Medicare).
Fee Maximum
See Fee Schedule.
The fee determined by an MCO to be acceptable for a procedure or service, which the physician agrees to accept as payment in full. Also known as a fee allowance, fee maximum, or capped fee.
FEHBP
See Federal Employee Health Benefits Plan.
FFS Payment System (PFFS)
See Private Fee-for-Service Plan (Medicare).
Finance Committee
Committee of the board of directors whose duty it is to review financial results, approve budgets, set and approve spending authorities, review the annual audit, and review and approve outside funding sources.
Finance Director
Chief financial officer responsible for the oversight of all financial and accounting operations, such as billing, management information services, enrollment, and underwriting as well as accounting, fiscal reporting, and budget preparation.
First Dollar Coverage
Refers to not having to meet a calendar year deductible prior to receiving reimbursement or payment for a medical service
A benefit program in which an employee has a choice of credits or dollars for distribution among various benefit options, e.g, health and disability insurance, dental benefits, child care, or pension benefits. See Cafeteria Plan or Flexible Spending Accounts (FSA).
Flexible Spending Accounts (FSA)
A flexible Spending Account is an employer-sponsored benefit which allows you to defer a portion of your paycheck into an account specifically intended to reimburse you for out of pocket costs. FSAs can be used for reimbursement of any medically related cost that is not covered by your health care plan, such as: deductibles and co-pays; birth control; Dental; Vision; etc. See Cafeteria Plan.
A listing of drugs, classified by therapeutic category or disease class, that are considered preferred therapy for a given managed population and that are to be used by an MCO´s providers in prescribing medications. Also see Drug.
Fraud
A false representation of a matter of fact (whether by words or conduct, by false or misleading allegations, or by concealment of that which should have been disclosed) which deceives and is intended to deceive another to his/her legal injury.
Free Look
The period during which you may reconsider the purchase of an insurance policy, cancel, and get a full refund. The clock starts running the day you receive the policy. Check your state´s insurance law for the specific provisions that apply in your state.
FSA
See Flexible Spending Accounts.
Full Dual Eligible
You will get the full amount of extra help, because you're Medicaid-eligible.
Full Subsidy Eligible
You will get the full amount of extra help, because you either have MSP, SSI, or you applied with Social Security.
Full Time Student
Under a health plan, an eligible dependant child student (typically age 19 or older) who meets the health plan´s criteria of "full-time." Such criteria normally typically includes minimum credit hour requirements (such as 12 credit hours in a semester) and a maximum age (age 23 is typical).
Full Time Employee
An employee who meets the eligibility requirements for full-time employees as outlined in the Benefit Agreement.
Fully Funded Plan
A health plan under which an insurer or MCO bears the financial responsibility of guaranteeing claim payments and paying for all incurred covered benefits and administration costs.
Functional Status
A patient´s ability to perform the activities of daily living.
Funding Vehicle
In a self-funded plan, the account into which the money that an employer and employees would have paid in premiums to an insurer or MCO is deposited until the money is paid out.
G . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W
Gag Rule Laws
Special laws that make sure that health plans let doctors tell their patients complete health care information. This includes information about treatments not covered by the health plan.
Gaps in Medicare Coverage (Click for Quote)
Services or costs that are not covered under Original Medicare plan like:
Medicare has built-in deductibles and coinsurance requirements that are higher today than ever before. To help control these costs, we offer these Medicare supplement plans to suit your personal needs.
- Deductibles
- Coinsurance & Copayments
- Dental Care
- Cosmetic Surgery
- Custodial Care
- Acupuncture
- Hearing Aids, hearing exams & screenings
- Routine eye care & most glasses
- Non-skilled care in nursing homes
- Most health care while traveling outside the United States
- Most outpatient prescription drugs
A primary care physician in a managed care environment who is responsible for managing the patient´s overall care and who must authorize all specialist referrals. In most health maintenance organizations (HMOs), the secondary care is not covered by insurance if the primary care physician does not approve it. See primary care physician
Generic Prescription Drug (Generic Drug) (Click here for more information)
The chemical equivalent to a Brand Name Drug. These drugs cost less, and the savings is passed onto health plan members in the form of a lower co-pay. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) rates these drugs to be as safe and effective as brand-name drugs.
Generic Substitution
The dispensing of a drug that is the generic equivalent of a drug listed on a pharmacy benefit management plan´s formulary. In most cases, generic substitution can be performed without physician approval.
Geographic Accessibility
Health plan accessibility, generally determined by drive time or number of primary care providers in a service area.
Global Bill
A total charge for a specific set of services, such as obstetrical services that encompass prenatal, delivery, and post-natal care
GPWW
See Group Practice without Walls.
Grace Period
A specified period of time after a premium is due during which you can still make a payment without losing the insurance. Check your policy to be sure what it provides.
Grievance Procedure
The required appeal process an HMO/insurance company provides to protest a decision regarding a claim payment.
Grievances
Formal complaints demanding formal resolution by a managed care plan.
Group Health Plan / Insurance (Click here for a quote).
A health plan that provides health coverage to employees and their families, and is supported by an employer or employee organization.
Group Insurance (Click here for a quote).
An insurance contract made with an employer or other entity that covers individuals in the group.
Group Market
A market segment that includes groups of two or more people that enter into a group contract with an MCO under which the MCO provides Health Care coverage to the members of the group.
An HMO that contracts with a multi-specialty group of physicians who are employees of the group practice. Also known as a group practice model HMO.
Group Practice Model HMO
See Group Model HMO.
Group Practice without Walls (GPWW)
A legal entity that combines multiple independent physician practices under one umbrella organization and performs certain business operations for the member practices or arranges for these operations to be performed. The GPWW may maintain its own facility for business operations or it may hire another company to provide this function.
Guaranteed Issue Health Insurance
Under guarantee issue, a health insurance company or HMO must issue coverage to an applicant regardless of prior medical history. In California, Illinois and Indiana, small employers (defined as 2 to 50 employees) cannot be refused coverage for their employees regardless of the medical history of one or more employees.
Guaranteed Issue Rights
Rights you have in certain situations when insurance companies are required by law to sell or offer you a Medigap policy. In these situations, an insurance company can't deny you a policy, or place conditions on a policy, such as exclusions for pre-existing conditions, and can't charge you more for a policy because of past or present health problems.
Guaranteed Renewable
An agreement by an insurance company to insure a person for as long as premiums are paid.
H . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W
Health Benefit Plan
A health insurance product offered by a health plan company that is defined by the benefit contract and represents a set of covered services and a provider network.
HCFA Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS)
Name given to CPT codes (Level I), alphanumeric codes (Level II), and local codes (Level III) used by payers and providers for billing purposes. Within the industry, most refer to Level II national codes as HCPCS codes.
HCPCS
See HCFA Common Procedure Coding System.
HCQIA
See Health Care Quality Improvement Act.
HCQIP
See Health Care Quality Improvement Program.
HDHP
See High Deductible Health Plan.
Health Care Financing Administration
The administration that oversees Medicare and Medicaid and also sets standards health care providers must meet in order to become certified as a qualified Medicare provider.
Health Care Quality
The degree to which health services for individuals and populations increase the likelihood of desired health outcomes and are consistent with current professional knowledge.
Legal document that lets you (“the principal”) appoint another person(s) (your “agent” or “attorney in fact”) to make health care decisions for you if you become too sick or disabled to make them yourself.
Health Care Provider
A doctor, hospital, laboratory, nurse, or anyone who delivers medical or health-related care.
Health Care Quality Improvement Act (HCQIA)
A federal act which exempts hospitals, group practices, and HMOs from certain antitrust provisions as they apply to credentialing and peer review so long as these entities adhere to due process standards that are outlined in the Act.
Health Care Quality Improvement Program (HCQIP)
A program, established by the Balanced Budget Act of 1997, that seeks to improve the quality of care provided to Medicare beneficiaries by requiring Medicare+Choice coordinated care plans to undergo periodic quality review by a peer review organization.
Health Care Reimbursement Accounts
Accounts that allow you to set aside pre-tax dollars to pay for medical care or costs. See Health Savings Account (HSA).
Health Employer Data and Information Set (HEDIS)
A set of standard performance measures that provides information about the quality of a health plan. These measures are used to compare managed care plans.
Health Information Network (HIN)
An electronic system that uses telecommunications devices to link various Health Care entities within a geographic region in order to exchange patient, clinical, and financial information in an effort to reduce costs and practice better medicine.
Health Insurance
Insurance against expenses incurred through illness of the insured. Provides compensation for medical expenses.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) (Click here for more information)
A federal act that protects people who change jobs, are self-employed, or who have pre-existing medical conditions. HIPAA standardizes an approach to the continuation of Health Care benefits for individuals and members of small group health plans and establishes parity between the benefits extended to these individuals and those benefits offered to employees in large group plans. The act also contains provisions designed to ensure that prospective or current enrollees in a group health plan are not discriminated against based on health status. In other words ... It allows people to buy individual health insurance when they lose their group health insurance, even if they have pre-existing health condidions. If you qualify, all health plans that sell individual plans MUST offer you health insurance. The purpose of the law is to:
- Improve portability and continuity of health insurance coverage in the group and individual markets
- To combat waste, fraud and abuse in health insurance and health care delivery
- To promote the use of medical savings accounts
- To improve access to long-term care services and coverage
- To simplify the administration of health insurance
Health Insurance Purchasing Co-Ops (HPCs)
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO)
Prepaid health plans which cover doctors´ visits, hospital stays, emergency care, surgery, preventive care, checkups, lab tests, X-rays, and therapy. In a HMO, one must choose a primary care physician who coordinates all care and makes referrals to any specialists that may be required. In a HMO, one must use the doctors, hospitals and clinics that participate in your plan´s network. No benefits are paid for non-emergency benefits provided outside the HMO network.
Health Reimbursement Arrangement (HRA)
A high deductible health insurance plan (sometimes called Section 125 plans) that provides savings that can be reimbursed to the employee as a tax deduction to the employer and not taxable to the employee. Funds placed into employee HRA accounts, along with premium fees and employee reimbursements, are tax-deductible. Unused HRA funds roll over on a yearly basis, and if left unused, continue to accrue until required. HRA funds can be used to pay for any tax-deductible medical expense. HRAs are similar to Flexible Spending Accounts (FSA); however, while an FSA is an add-on to your already existing medical coverage, an HRA is your medical coverage.
Health Savings Account (HSA) (Click here for more information)
Operating similarly to IRAs, HSAs are tax-advantaged savings accounts for health care services. A person must enroll in a qualified High-Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) before they can establish an HSA. An HSA (Health Savings Account) offers maximum cost effectiveness for your benefits plan. It gives your employees an account called a Health Savings Account, or HSA, which they can use to pay for their medical care and prescriptions. The HSA is funded by an employees´ pre-tax contributions, and you can also choose to make employer contributions. It also includes a Traditional Health Coverage (PPO) component, similar to a typical health plan, to help protect your employees against large health expenses.
The difference between an HSA and a HIA plan:
- With an HSA you put pre-tax dollars into the account. The money can be used for any medical expense (as defined by the IRS) tax exempt. The money is yours to do as you wish within the guidelines, but if you use the money for something non-medical you'll have taxes and possible penalties. If you leave the plan the money can be rolled over into another HSA or into an IRA.
- The big difference is the HIA is not tax qualified and the funds in the account are not yours. With an HIA the insurance company puts money into your account. You must use the money only for covered expenses. The money is forfeited if you leave the plan.


Hearing Services
Testing and services related to hearing.
HEDIS
See Health Employer Data and Information Set.
High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP)
A person must be enrolled in a qualified High-Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) before they can establish a Health Savings Account (HSA). Not all high-deductible health plans qualify for purposes of establishing HSA eligibility. A qualified HDHP benefit design must conform to various federally-mandated requirements, such as a minimum $1000 deductible and a lack of first-dollar benefit provisions.
HIN
See Health Information Network.
HIPAA
See Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act.
HMO
See Health Maintenance Organization.
HMO Act
1973 federal law that ensured access for HMOs to the employer-based insurance market.
Hold Harmless Provision
A contract clause which forbids providers from seeking compensation from patients if the health plan fails to compensate the providers because of insolvency or for any other reason.
Services given at home to aged, disabled, sick, or convalescent individuals not needing institutional care. The most common types of home care are visiting nurse services and speech, physical, occupational, and rehabilitation therapy. These services are provided by home health agencies, hospitals, or other community organizations.
Home Health Care Agency
A public or privage agency that specializes in providing home health care. See Home Health Care.
Home Infusion Therapy
The administration of intravenous drug therapy in the home. Home infusion therapy includes the following services: solutions and pharmaceutical additives; pharmacy compounding and dispensing services; durable medical equipment; ancillary medical supplies; and nursing services.
Medicare’s home health benefit provides skilled nursing and other services to beneficiaries who are "homebound," that is, able to leave home only with great difficulty and for absences that are infrequent and of short duration.
Homemaking Services
See Custodial Care.
Care for the terminally ill and their families, in the home or a non-hospital setting, that emphasizes alleviating pain rather than a medical cure. As of June 1, 2010, this is a standard coverage on all Medigap policies.
Hospital
An institution whose primary function is to provide inpatient services, diagnostic and therapeutic, for a variety of medical conditions, both surgical and non-surgical. In addition, most hospitals provide some outpatient services, particularly emergency care.
Hospital Care
Reimbursement for both inpaient and outpatient medical care expenses incurred in a hospital. Inpatient Benefits include; Charges for room and board, charges for necessary services and supplies sometimes referred to as ´hospital extras,´ ´other hospital extras,´ ´miscellaneous charges,´ and ´ancillary charges. Outpatient Benefits include; surgical procedures, rehabilitation therapy, and physical therapy.
Hospital Indemnity Policy
Pays a fixed dollar amount for each day you are hospitalized, regardless of the actual costs.
Hospital Outpatient
A patient who is receiving care at a hospital or other health facility, without being admitted to the facility.
Hospital Pre-Certification
Managed care plans often require prior approval before the insured enters the hospital. In the case of an emergency, or other situation where pre-certification is not possible, such plans often require prompt notification often in 48 hours after admission.
Hospital Surgical Coverage
A form of health insurance that offers coverage of certain costs related to hospitalization and surgical procedures. A hospital-surgical plan does not cover other types of medical services, such as physician office visits and outpatient prescription drugs.
HRA
See Health Reimbursement Arrangement.
HSA
I . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W
IBNR Claims
See Incurred but not Reported Claims.
ID Card / Identification Card
Card given to insured individuals which advises medical providers that a patient is covered by a particular health insurance plan.
IDS
See Integrated Delivery System.
Immunizations
Specific types of injections to prevent infectious diseases and viral infections.
In-Network
Describes a provider or health care facility which is part of a health plan´s network. When applicable, insured individuals usually pay less when using an in-network provider.
Incorporation by Reference
The method of making a document a part of a contract by referring to it in the body of the contract.
Incurred but not Reported (IBNR)
The actuarial estimate of amounts required to pay ultimate net losses after netting out existing amounts on reported but unpaid claims. The IBNR estimate includes an allowance for potential changes in such existing amounts as well as additional amounts for claims that have already occurred but are yet to be reported.
Incurral Date
The date on which health care services are provided to a covered person. The incurral date, not the date on which the insurance company pays a health care claim, is the critical date in determining health insurance benefits. For example, a health insurance company will not pay a claim for health care services incurred prior to the effective date of the health insurance coverage.
Indemnity
Term used to describe a benefit that pays a specific dollar amount (typically by reimbursement) rather than actual charges or a percentage of the charges. This type of health insurance coverage can leave the insured with more out-of-pocket exposure because there aren't any network negotiated rates and the insured is responsible for any charges above the specific dollar amount that the insurance company reimburses.
Indemnity Insurance Health Plan
Indemnity health insurance plans are also called "fee-for-service." These are the types of plans that primarily existed before the rise of HMOs and PPOs. With indemnity plans, the individual pays a pre-determined percentage of the cost of health care services, and the health plan pays the other percentage. For example, an individual might pay 20% for services and the insurance company pays 80%. The fees for services are defined by the health care providers and vary from physician to physician and hospital to hospital.
Indemnity Wraparound Policy
An out-of-plan product that an HMO offers through an agreement with an insurance company.
Independent Agents
Agents that represent the products of several health plans or insurers. See Agent.
Independent / Individual Practice Association (IPA)
An organization comprised of individual physicians or physicians in small group practices that contracts with MCOs on behalf of its member physicians to provide Health Care services.
Independent Reviewer (IRE)
An independent reviewer, also known as an independent review entity (IRE), is an outside organization that has a contract with Medicare. If you appeal a decision about your coverage or if your plan doesn't make a timely appeals decision, the IRE may review your case. The IRE has no connection to the plan. Refer to your plan's explanation of coverage for more details about the appeals process. Click here for more information on Medicare appeals.
Individual Deductible
Amount of eligible expense a covered person must pay each year before the health plan will pay for eligible benefits.
Individual Health Insurance (Click here for a quote).
Health insurance coverage on an individual, not group, basis. The premium is usually higher for individual health insurance than for a group policy, but you may not qualify for a group plan.
Individual Market
A market segment composed of customers not eligible for Medicare or Medicaid who are covered under an individual contract for health coverage.
Individual Policy
See Individual Health Insurance.
A type of stop-loss insurance that provides benefits for claims on an individual that exceed a stated amount in a given period. Also known as specific stop-loss coverage.
Infertility
Term used to describe the inability to conceive or an inability to carry a pregnancy to a live birth. Also includes the presence of a condition recognized by a physician as the cause of infertility.
Infusion Therapy
The administration of intravenous drug therapy. Infusion therapy includes the following services: solutions and pharmaceutical additives; pharmacy compounding and dispensing services; durable medical equipment; ancillary medical supplies; and nursing services.
Initial Coverage Election Period (Medicare)
When you reach age 65 and you sign up for Medicare Part B, you have a one-time seven-month period (three months before, three months after and the month of your birthday) during which you may purchase any Medigap (or Medicare Advantage) policy a company sells at the lowest price available, even if you have or used to have health problems. If you enroll during this time, the insurance company cannot:
If you purchase a Medigap (or Medicare Advantage) policy after this seven-month initial enrollment period, you could be denied the Medigap (or Medicare Advantage) policy of your choice, or any Medigap (or Medicare Advantage) policy, because of pre-existing health conditions.
- deny you medigap coverage or make you wait for coverage to start; or
- charge you more for a policy because of past or present health problems.
Inpatient / Inpatient Care
Health care that you get when you stay overnight (24 hours) in a hospital.
A person who has obtained health insurance coverage under a health insurance plan.
Integrated Delivery System (IDS)
A provider organization that is fully integrated operationally and clinically to provide a full range of Health Care services, including physician services, hospital services, and ancillary services.
Integration
For provider organizations, the unification of two or more previously separate providers under common ownership or control, or the combination of the business operations of two or more providers that were previously carried out separately and independently.
Intermediate Nursing Care
Health care for individuals who need minimum supervision.
International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM)
Coding system maintained by the National Center for Health Statistics and the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). This coding system differentiates diagnostic conditions and is used by hospitals, governments, health insurance plans, and health care providers around the world.
Investigative Procedures or Medications
Those that have progressed to limited use on humans, but which are not widely accepted as proven and effective within the organized medical community.
IPA
See Independent Practice Association.
IPA Model HMO
A health maintenance organization which contracts with one or more associations of physicians in independent practice who agree to provide medical services to HMO members.
J . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W
Joint Commission on Accreditation of Health care Organizations (JCAHO)
Commission responsible for the accreditation of health care organizations after careful evaluation of the services provided to determine quality care.
Joint Venture
A type of partial structural integration in which one or more separate organizations combine resources to achieve a stated objective. The participating companies share ownership of the venture and responsibility for its operations, but usually maintain separate ownership and control over their operations outside of the joint venture.
L . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W
Large Group
A large pool of individuals for which health coverage is provided by the group sponsor. A large group may be defined as more than 50, 250, 500, 1,000, or some other number of members, depending on the MCO.
Lifetime Maximum Benefit
A cap on the benefits paid for the duration of a health insurance policy. Many policies have a lifetime limit of $5 million, which means that the insurer agrees to cover up to $5 million in covered services over the life of the policy. Once the $5 million maximum is reached, no additional benefits are payable.
Under Medicare, 60 extra non-renewable days of hospitalization coverage available for use if a hospital stay exceeds the 90 days available in a benefit period. Once a reserve day is used, it is gone for life. Also called Reserve Days.
Limitations
A restriction on the amount of benefits paid out for a particular covered expense.
Limited Health Insurance Policy
A policy that covers only specified accidents or sicknesses (e.g. a cancer policy).
Living Will
A legal document in which a competent person directs in advance that artificial life-prolonging treatment not be used if he or she has or develops a terminal and irreversible condition and becomes incompetent to make health care decisions.
Long-Term Care
Care for patients with chronic diseases or disabilities including home health care, adult day care, hospice care, respite care, and intermediate care but not hospital care.
Long-Term Care Facility
See Nursing Home.
Long-Term Care Policy
Insurance policies that cover specified services for a specified period of time. Long-term care policies (and their prices) vary significantly. Covered services often include nursing care, home health care services, and custodial care.
Disability income insurance which typically provides disability income benefits that begin at the end of a specified waiting period and that continue until the earlier of the date when the insured person returns to work, dies, or becomes eligible for pension benefits. See also disability income insurance and short-term disability income insurance.
Loss
The basis for a claim under an insurance policy.
Loss Rate
The number and timing of losses that will occur in a given group of insureds while the coverage is in force.
Loss Ratio
The dollar amount an insurer pays in claims compared to the amount it collects in premiums.
Lou Gehrig’s Disease/ALS
See ALS.
LTD
M . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W
MA
Medicare Advantage plan (Medicare Part C) with no drug coverage.
Medicare Advantage plan (Medicare Part C) with drug coverage (Medicare Part D) benefits built in.
Mail-Order Pharmacy Programs
Programs that offer drugs ordered and delivered through the mail to plan members at a reduced cost.
Major Medical Insurance
Health insurance coverage for expenses associated with hospital confinements, surgeries and/or medical conditions requiring a broad range of medical services and supplies.
Managed Behavioral Health Organization (MBHO)
An organization that provides behavioral health services using managed care techniques.
Managed Care
The integration of both the financing and delivery of Health Care within a system that seeks to manage the accessibility, cost, and quality of that care.
Managed Care Organization (MCO)
Comprehensive health insurance plans provided to participating members of a health care organization. Managed care plans are organized into a network of providers, including physicians and hospitals. Common types of managed care plans are health maintenance organizations (HMOs), preferred provider organizations (PPOs), and point of service (POS) plans. Also known as a managed care plan.
Managed Care Plan
See Managed Care Organization (MCO).
Managed Dental Care
Any dental plan offered by an organization that provides a benefit plan that differs from a traditional fee-for-service plan.
Managed Indemnity Plans
Health insurance plans that are administered like traditional indemnity plans but which include managed care "overlays" such as precertification and other utilization review techniques.
Management Services Organization (MSO)
An organization, owned by a hospital or a group of investors, that provides management and administrative support services to individual physicians or small group practices in order to relieve physicians of non-medical business functions so that they can concentrate on the clinical aspects of their practice.
Mandated Benefits
Health care benefits that state or federal law says must be include din health care plans.
Manual Rating
A rating method under which a health plan uses the plan´s average experience with all groups - and sometimes the experience of other health plans - rather than a particular group´s experience to calculate the group´s premium. An MCO often lists manual rates in an underwriting or rating manual.
Market Segmentation
The process of dividing the total market for a product or service into smaller, more manageable subsets or groups of customers.
Subsets or manageable groups of customers in a total market.
Marketing Director
Individual responsible for marketing a managed care plan, whose duties include oversight of marketing representatives, advertising, client relations, and enrollment forecasting.
Maximum Out-Of-Pocket (OOP) Sxpenses
See Out-Of-Pocket (OOP) Maximum/Limit.
Maternity Care
The care of women before and during childbirth as well as the care of newborn babies.
MBHO
See Managed Behavioral Health Organization.
McCarran-Ferguson Act
A federal act that placed the primary responsibility for regulating health insurance companies and HMOs that service private sector (commercial) plan members at the state level.
MCO
See Managed Care Organization.
Medi-Medi
People who qualify for both Medicare and full Medi-Cal (Medicaid) are known as "dual eligibles" or "Medi-Medis."
Medicaid
A jointly funded federal and state program that provides hospital expense and medical expense coverage to the low-income population and certain aged and disabled individuals. Known in California as "Medi-Cal."
Medical Advisory Committee
Committee whose purpose is to review general medical management issues brought to it by the medical director.
Medical Center
See Ambulatory Care Facility (ACF).
Medical Clinic
See Ambulatory Care Facility (ACF).
Medical Director
Manager in a Health Care organization responsible for provider relations, provider recruiting, quality and utilization management, and medical policy.
Medical Equipment
See Durable Medical Equipment.
Medical Foundation
A not-for-profit entity, usually created by a hospital or health system, that purchases and manages physician practices.
See Consolidated Medical Group.
Medical Loss Ratio
The ratio between the cost to deliver medical care and the amount of money that was taken in by a plan. Insurance companies often have a medical loss ratio of 96 percent or more: tightly managed HMOs may have medical loss ratios of 75 percent to 85 percent, although the administrative cost ratio is also higher.
Medical Necessity
Medical information justifying that the service rendered or item provided is reasonable and appropriate for the diagnosis or treatment of a medical condition or illness
Medically Necessary
Many insurance policies will pay only for treatment that is deemed "medically necessary" to restore a person´s health. For instance, many health insurance policies will not cover routine physical exams or plastic surgery for cosmetic purposes.
A trust that employees of small businesses may establish to pay for out-of-pocket medical expenses. MSAs cannot be established after 2007 and have been replaced by health savings accounts (HSAs), which were introduced in 2003.
Medicare Medical Savings Account (MSA)
A Medicare MSA is a high deductible health plan combined with a savings account for health care expenses. Medicare makes a contribution to the beneficiary's savings account.
- MSA enrollees pay for health care expenses from the savings account and then out-of-pocket until the annual deductible is met, after which the plan pays 100% for covered services.
- MSAs cover Part A and Part B benefits, but not Part D Medicare prescription drug benefits.
- Enrollees pay the Part B premium and any premium for supplemental benefits.
- The maximum deductible for MSA plans in 2018 is $11,980 and $12,650 in 2019.
Medical Underwriting
The evaluation of health questionnaires submitted by all proposed plan members to determine the insurability of the group.
Medically Needy Individuals
Enrollees in Medicaid programs whose income or assets exceed the maximum threshold for certain federal programs.
A federal government hospital expense and medical expense insurance plan primarily for elderly (age 65 or older) and disabled persons. See also Medicare Part A, Medicare Part B, Medicare Part C, and Medicare Part D.
A private health plan that provides the same coverage as Medicare Part A, Medicare Part B, and typically some additional benefits (such as Part D).
With Medicare Advantage Plans you won't need to buy a Medigap policy.:
- You generally get all your Medicare-covered health care through that plan.
- Coverage may include prescription drug coverage.
- You may get extra benefits, such as coverage for vision, hearing, dental, and/or health and wellness programs.
- You may have lower out-of-pocket costs than Original Medicare.
- You may have to use the plan's doctors and hospitals to get services.
Medicare Card
Also known as the “red, white and blue card.” Everyone who enrolls in Medicare receives a Medicare card. It lists your name and the dates that your Original Medicare hospital insurance (Part A) and medical insurance (Part B) began. It also shows your Medicare claim number, which is the same as your Social Security number and identifies you in the Medicare system. If you choose to get your Medicare benefits from a Medicare private health plan (Part C), you will use your plan’s card instead of the Medicare card.
Medicare Dual Eligible Beneficiaries
Beneficiaries who qualify for both Medicare and Medicaid are considered "dual eligible" individuals. Key issues that are important to dual eligible beneficiaries considering MA enrollment include:
- Whether the beneficiary is eligible for medical benefits under Medicaid. Medicaid may provide additional benefits, but Medicaid will only pay if the services are furnished by Medicaid participating providers.
- For services covered under Medicare and Medicaid, most dual eligibles will not have to pay cost sharing more than the Medicaid cost sharing amounts for the services.
- Whether the MA plan's network providers accept both Medicare and Medicaid patients.
- Whether the beneficiary will need help to find providers who accept both Medicare and Medicaid.
- Whether a single Medicare-Medicaid plan that combines Medicare and Medicaid benefits is available to the beneficiary.
The part of Medicare that provides basic hospital insurance coverage automatically for most eligible persons. See also Medicare.
A voluntary program that is part of Medicare and provides benefits to cover the costs of physicians´ services. See also Medicare.
The part of Medicare that expands the list of different types of entities allowed to offer health plans to Medicare beneficiaries. Also known as Medicare+Choice. See also Medicare.
A private plan that offers coverage for prescription drugs. Medicare beneficiaries may enroll in a stand-alone Prescription Drug Plan (PDP) or a Medicare Advantage plan with prescription drug coverage (MA-PD). These plans are regulated by the federal government, but sold and managed by private insurance carriers.
Medicare+ Choice
See Medicare Part C.
Medicare Fraud
Medicare fraud is a general term that refers to an individual or corporation that seeks to collect Medicare health care reimbursement under false pretenses.
Medicare Prescription Drug Plan (Part D)
See Medicare Part D.
Medicare Private Health Plan
See Medicare Part C.
A supplemental insurance policy to help cover the difference between approved medical charges and benefits paid by Medicare. These plans are also known as Medi-Gap plans.
Medicare-approved Amount
In Original Medicare, this is the amount a doctor or supplier can be paid, including what Medicare pays and any deductible, coinsurance, or copayment that you pay. It may be less than the actual amount charged by a doctor or supplier.
Medigap (Click for Quote)
A supplemental insurance policy to help cover the difference between approved medical charges and benefits paid by Medicare. These plans are also known as Medicare Supplement plans. As of June 1, 2010 there are now 10 Medigap plans.

Member
An individual or dependent who is enrolled in and covered by a health care plan. Also called enrollee or beneficiary. See Insured.
Member Services
The department responsible for helping members with any problems, handling member grievances and complaints, tracking and reporting patterns of problems encountered, and enhancing the relationship between members of the plan and the plan itself.
Mental Health / Behavioral Health
Conditions that affect thinking and the ability to figure things out which affect perceptions, mood and behavior. Such disorders are recognized primarily by symptoms or signs that appear as distortions of normal thinking or distortions of the way things are perceived (seeing or hearing things that are not there). Disorders can also be recognized by moodiness, sudden or extreme changes in mood, depression, and highly agitated or unusual behavior.
Mental Health Parity Act (MHPA)
A federal act which prohibits group health plans that offer mental health benefits from applying more restrictive limits on coverage for mental illness than for physical illness.
Merger
A type of structural integration that occurs when two or more separate providers are legally joined.
Messenger Model
A type of independent practice association (IPA) that simply negotiates contract terms with MCOs on behalf of member physicians, who then contract directly with MCOs using the terms negotiated by the IPA. This type of IPA is most often used with fee-for-service or discounted fee-for-service compensation arrangements.
MET
MHPA
Modified Community Rating
See Adjusted Community Rating.
Monthly Operating Report (MOR)
A document that reports the month and year-to-date financial status of a managed care plan.
Monthly Premium
A premium is the monthly fee that is paid to an insurance company or health plan to provide health coverage, including paying for health-related services such as doctor visits, hospitalizations, and medications.
MOR
MSA
MSO
See Management Services Organization.
An arrangement created to obtain health and other benefits for participating employer groups. Small employers can pool their contributions to receive the advantages of large group underwriting.
Affordable Health Insurance Online
N . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W
NAIC
See National Association of Insurance Commissioners.
National Accounts
Large group accounts that have employees in more than one geographic area that are covered through a single national contract for health coverage. Contrast with large local groups.
National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC)
A national organization of state officials charged with regulating insurance. NAIC was formed to promote national uniformity in insurance regulations.
National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA)
A national group responsible for devising and monitoring quality measurements and standards for health care entities.
Numerical coding system for drug identification. NDC numbers are assigned by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and are typically used to bill payers for the drugs provided to health care beneficiaries.
National Practitioner Data Bank (NPDB)
A database maintained by the federal government that contains information on physicians and other medical practitioners against whom medical malpractice claims have been settled or other disciplinary actions have been taken.
NCQA
See National Committee for Quality Assurance.
NDC
Negotiated Fee / Rate
The amount participating providers agree to accept as payment in full for covered services. It is usually lower than their normal charge. Negotiated rates are determined by Participating Provider Agreements.
Network
The group of physicians, hospitals, and other medical care providers that a specific managed care plan has contracted with to deliver medical services to its members.
Network Model HMO
An HMO that contracts with more than one group practice of physicians or specialty groups.
Network Provider
Physicians, hospitals or other providers of medical services that have agreed to participate in a network, to offer their services at negotiated rates, and to meet other negotiated contractual provisions. Also called "participating provider."
Newborns´ and Mothers´ Health Protection Act (NMHPA)
A federal law which mandates that coverage for hospital stays for childbirth cannot generally be less than 48 hours for normal deliveries or 96 hours for cesarean births.
NMHPA
See Newborns´ and Mothers´ Health Protection Act.
No Balance Billing Provision
A provider contract clause which states that the provider agrees to accept the amount the plan pays for medical services as payment in full and not to bill plan members for additional amounts (except for copayments, coinsurance, and deductibles).
Non-Cancellable Policy
A policy that guarantees you can receive insurance, as long as you pay the premium. It is also called a guaranteed renewable policy.
Non-Formulary Drugs
Any prescription drug that is not included on your health plan´s list of approved medications.
Non-Group Market
A market segment that consists of customers who are covered under an individual contract for health coverage or enrolled in a government program.
Non-Maleficence
An ethical principle which, when applied to managed care, states that managed care organizations and their providers are obligated not to harm their members.
Non-Participating Provider
A medical provider who has not contracted with a carrier or health plan to be a participating provider.
A network pharmacy that offers covered drugs to plan members at higher out-of-pocket costs than what the member would pay at a preferred network pharmacy.
NPDB
See National Practitioner Data Bank.
A licensed facility that provides general nursing care to those who are chronically ill or unable to take care of daily living needs. May also be referred to as a Long Term Care Facility.
Nursing Home Insurance
Insurance that only covers, or primarily, care in a nursing home. The terms nursing home insurance and long-term care insurance are sometimes loosely used interchangeably.
O . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W
OBRA
See Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1990.
Occupational therapy
Treatment to restore a physically disabled person´s ability to perform activities such as walking, eating, drinking, toileting and bathing.
Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (OBRA) of 1990
A federal act which established the Medicare SELECT program, a Medicare supplement that uses a preferred provider organization to supplement Medicare Part B coverage.
OEP
OOP
See Out-Of-Pocket.
Open Access
A provision that specifies that plan members may self-refer to a specialist, either in-network or out-of-network, at full benefit or at a reduced benefit, without first obtaining a referral from a primary care provider.
A period each year during which employees have an opportunity to change their employer-provided health care coverage. They usually can choose among various plans from different health insurance providers between November 15-December 31 for Medigap, Medicare Advantage AND Medicare prescription drug coverage; January 1-March 31 Open Enrollment Period for Medicare Advantage Plans only.
Open Formulary
The provision that drugs on the preferred list and those not on the preferred list will both be covered by a PBM or MCO.
Open-Panel HMO
An HMO in which any physician who meets the HMO´s standards of care may contract with the HMO as a provider. These physicians typically operate out of their own offices and see other patients as well as HMO members.
Open PHO
A type of physician-hospital organization that is available to all of a hospital´s eligible medical staff.
Operational Integration
The consolidation into a single operation of operations that were previously carried out separately by different providers.
Operations Director
Individual who typically oversees claims, management information services, enrollment, underwriting, member services, and office management.
Also known as "Traditional Medicare." The federal health insurance program, created in 1965, under which the government pays providers directly for each service a person receives (on a fee-for-service basis). Almost all doctors and hospitals in the United States accept Original Medicare. The majority of people with Medicare are enrolled in Original Medicare, as opposed to a Medicare private health plan (Part C). Also see Medicare.
Outcomes Measures
Health Care quality indicators that gauge the extent to which Health Care services succeed in improving patient health.
Out-of-Network
Health care services received outside the HMO or PPO network. A health care provider with whom a managed care organization does not have a contract to provide health care services. Because the beneficiary must pay either all of the costs of care from an out-of-network provider or their cost-sharing requirements are greatly increased, depending on the particular plan a beneficiary is in.
Out-of-Plan
This phrase usually refers to physicians, hospitals or other health care providers who are considered non-participants in an insurance plan (usually an HMO or PPO). Depending on an individual´s health insurance plan, expenses incurred by services provided by out-of-plan health professionals may not be covered, or covered at a reduced benefit level.
Out-of-Pocket Costs
Insured health care costs for which one is responsible, because of the application of deductibles, coinsurance and co-payments.
Out-Of-Pocket (OOP) Maximum/Limit
Total dollar amount an insured will be required to pay for covered medical services during a specified period, such as one year. The out-of-pocket maximum may also be called the stop-loss limit or catastrophic expense limit.
Outpatient
A patient who is receiving ambulatory care at a hospital or other health facility without being admitted to the facility.
Outpatient Care
Treatment that is provided to a patient who is able to return home after care without an overnight stay in a hospital or other inpatient facility.
Outpatient Services
Services usually provided in clinics, physician or provider officers, ambulatory surgical centers, hospices, home health services, etc.
Outpatient Surgery
Surgical procedures performed that do not require an overnight stay in the hospital or ambulatory surgery facility. Such surgery can be performed in the hospital, a surgery center or physician office.
Over-the-Counter Drugs
Any drug that you can buy, without a prescription, at your local pharmacy or drug store. These drugs are not covered by the Medicare prescription drug benefit (Part D).
P . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W
Palliative Care
Care of patients with a terminal illness directed towards relief of symptoms without attempting to be curative.
Parent Company
A company that owns another company.
Partial Day Treatment
A program offered by appropriately licensed psychiatric facilities that includes either a day or evening treatment program for mental health or substance abuse. Such care is an alternative to inpatient treatment.
Participating Hospital
A hospital that has entered into an agreement to provide hospital services as a participating provider. The hospital, by entering into the agreement, is a participating hospital for all members and covered persons.
Participating Medical Group (PMG)
A group of physicians and specialist who practice together and provide most services (including X-ray and lab) - all at the same location.
Participating Provider
A health care provider who has been contracted to render medical services or supplies to insured persons at a pre-negotiated fee. Providers include hospitals, physicians, and other medical facilities that are part of a PPO or HMO network.
Patient Bill of Rights
Refers to the Consumer Bill of Rights and Responsibilities, a report prepared by the President´s Advisory Commission on Consumer Protection and Quality in the Health Care Industry in an effort to ensure the security of patient information, promote Health Care quality, and improve the availability of Health Care treatment and services. The report lists a number "rights," subdivided into eight general areas, that all Health Care consumers should be guaranteed and describes responsibilities that consumers need to accept for the sake of their own health.
Patient Perception
A type of outcomes measure related to how the patient feels after treatment.
PBM plan
See Pharmacy Benefit Management plan.
PCCM
See Primary Care Case Manager.
PCP
PDP (Stand alone Prescription Drug Plan)
If you are a Medicare beneficiary, you are eligible for Medicare prescription drug coverage, regardless of your income, health status, or current prescription expenses. These plans add prescription drug coverage to Original Medicare, and certain types of Medicare Health Plans (Medigap).
Peer Review
The analysis of a clinician´s care by a group of that clinician´s professional colleagues. The provider´s care is generally compared to applicable standards of care, and the group´s analysis is used as a learning tool for the members of the group.
Peer Review Organizations (PROs)
According to the Balanced Budget Act of 1997, organizations or groups of practicing physicians and other Health Care professionals paid by the federal government to review and evaluate the services provided by other practitioners and to monitor the quality of care given to Medicare patients.
Pended
A claims term that refers to a situation in which it is not known whether an authorization has or will be issued for delivery of a Health Care service, and the case has been set aside for review.
Performance Measures
Quantitative measures of the quality of care provided by a health plan or provider that consumers, payors, regulators, and others can use to compare the plan or provider to other plans and providers.
Personal Care (also called Custodial Care)
Care to help individuals meet personal activities of daily living needs. Someone without professional training may provide care. Medicare only covers personal care if you are homebound and receiving skilled care.
Personal Care Attendant
A certified or qualified aide affiliated with home health care agency whose responsibility is to provide assistance with health care, such as aid in performing activities of daily living.
Personal Care Physician
Personal Care Provider
PFFS / Private Fee-For-Service
See Private Fee-for-Service Plan (Medicare).
Identification cards issued by a pharmacy benefit management plan to plan members. These cards assist PBMs in processing and tracking pharmaceutical claims. Also known as drug cards or prescription cards.
Pharmacotherapy
The use of drugs to treat a disease or condition.
Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee
Committee charged with developing a formulary, reviewing changes to that formulary, and reviewing abnormal prescription utilization patterns by providers.
Pharmacy Benefit Management (PBM) plan
A type of managed care specialty service organization that seeks to contain the costs, while promoting safer and more efficient use, of prescription drugs or pharmaceuticals. Also known as a prescription benefit management plan.
PHO
See Physician-Hospital Organization.
Physical Examination
Physical examination, as well as information about your medical history, may be required to qualify for health insurance. The requirements will vary for individual or group coverage, for different insurance companies, and for very large or very small groups.
Physical Therapy
Treatment involving physical movement to relieve pain, restore function and prevent disability following disease, injury or loss of limb.
Physician-Hospital Organization (PHO)
A joint venture between a hospital and many or all of its admitting physicians whose primary purpose is contract negotiations with MCOs and marketing.
Physician Practice Management (PPM) Company
A company, owned by a group of investors, that purchases physicians´ practice assets, provides practice management services, and, in most cases, gives physicians a long-term contract to continue working in their practice and sometimes an equity (ownership) position in the company.
In the context of a pharmacy benefit plan, the process of compiling data on physician prescribing patterns and comparing physicians´ actual prescribing patterns to expected patterns within select drug categories. Also known as profiling.
Plan Administration
Overseeing the details and routine activities of installing and running a health plan, such as answering questions, enrolling new individuals for coverage, billing and collecting premiums, etc.
Plan Benefit Maximum
Maximum amount the carrier will pay toward an individual´s coverage. The amount varies depending on the type of coverage the individual carries.
Plan Funding
The method that an employer or other payor or purchaser uses to pay medical benefit costs and administrative expenses.
A physician's written plan describing the type and frequency of services and care a particular patient needs.
A POS (Point of Service) is an "HMO/PPO" hybrid; sometimes referred to as an "open-ended" HMO when offered by an HMO. POS plans resemble HMOs for in-network services. Services received outside of the network are usually reimbursed in a manner similar to conventional indemnity plans (e.g., provider reimbursement based on a fee schedule or usual, customary and reasonable charges).
Policy
The insurance agreement or contract.
Pooling
The practice of underwriting a number of small groups as if they constituted one large group.
Portability.
The ability for an individual to transfer from one health insurer to another health insurer with regard to pre-existing conditions or other risk factors.
POS
Power of Attorney
See Health Care Power of Attorney.
PPA
See Preferred Provider Arrangement.
PPM
See Physician Practice Management Company.
PPO
See Preferred Provider Organization.
Practice Guideline
See Clinical Practice Guideline.
Preferred Pharmacy
A network pharmacy that offers covered drugs to plan members at lower out-of-pocket costs than what the member would pay at a non-preferred network pharmacy.
Preferred Provider Arrangement (PPA)
As defined in state laws, a contract between a Health Care insurer and a Health Care provider or group of providers who agree to provide services to persons covered under the contract. Examples include preferred provider organizations (PPOs) and exclusive provider organizations (EPOs).
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)
A Health Care benefit arrangement designed to supply services at a discounted cost by providing incentives for members to use designated Health Care providers (who contract with the PPO at a discount), but which also provides coverage for services rendered by Health Care providers who are not part of the PPO network.
Pregnancy Care
Federal maternity legislation, enacted in 1978, requires that employers engaged in interstate commerce who have 15 or more employees provide the same benefits for pregnancy, childbirth, and related medical conditions as for any other sickness or injury. This includes all employers who are, or become, subject to Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964.
Premium
A prepaid payment or series of payments made to a health plan by purchasers, and often plan members, for medical benefits.
Premium Taxes
State income taxes levied on an insurer´s premium income.
Premium Only Plan (POP)
Premium Only Plan (POP) is a provision of Section 125 of the Internal Revenue Code, in which the total taxable payroll of a company is reduced by the amount of their employees´ premium contributions. The savings to the employer depends on the total company payroll and the dollar amount employees contribute toward their benefits. Employees use pre-tax dollars to pay their share of monthly premiums, which in turn lowers their FICA, federal and applicable state/local taxes. The result is reduced payroll taxes for the employer and increased take-home pay for the employee.
Prepaid Care
Health Care services provided to an HMO member in exchange for a fixed, monthly premium paid in advance of the delivery of medical care.
Prepaid Group Practices
Term originally used to describe Health Care systems that later became known as health maintenance organizations.
Prescription
A written order or refill notice issued by a licensed medical professional for drugs which are only available through a pharmacy.
Prescription Benefit Management Plan
See pharmacy benefit management plan.
Prescription Cards
Prescription Drugs, Brand Name and Generic
A brand name drug is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and is supplied by one company (the pharmaceutical manufacturer). The drug is protected by a patent and is marketed under the manufacturer´s brand name.
When a drug patent expires, other companies may produce a generic version of the brand name drug. A generic medication, also approved by the FDA, is basically a copy of the brand name drug and is marketed under its chemical name. A generic drug may have a different color or shape than its brand name counterpart, but it must have the same active ingredients, strength, and dosage form (i.e., pill, liquid, or injection).Prescription Drug Formulary
The list of prescription drugs covered by an insurance company.
Prescription Drug Insurance
Health coverage that helps you pay for prescription drugs. With a prescription drug insurance plan, you generally pay a copayment for each prescription drug you get that is covered by your plan. If you have Medicare, you can get prescription drug insurance through Part D, the Medicare prescription drug benefit.
Preventive Care
An approach to health care which emphasizes preventive measures and health screenings such as routine physicals, well-baby care, immunizations, diagnostic lab and x-ray tests, pap smears, mammograms and other early detection testing. The purpose of offering coverage for preventive care is to diagnose a problem early, when it is less costly to treat, rather than late in the stage of a disease when it is much more expensive, or too late to treat.
Pre-Admission Review
A review of an individual´s health care status or condition, prior to an individual being admitted to a hospital or inpatient health care facility. Pre-admission reviews are often conducted by case managers or insurance company representatives (usually nurses) in cooperation with the individual, his or her physician or health care provider, and hospitals.
Pre-Admission Testing
Medical tests that are completed for an individual prior to being admitted to a hospital or inpatient health care facility
Pre-Approval
Pre-Authorization
Under a pre-authorization provision of a health insurance policy, the insured must contact the health insurance company prior to a hospitalization or surgery, and receive authorization for the service.
This is a requirement that a insured person call their health insurance company and advise them a doctor has stated certain medical treatment is required. This is done before receiving treatment from the doctor or hospital. A health insurance policy will normally list the medical conditions that require pre-certification before receiving treatment. When pre-certification is not received, benefits will be reduced or possibly not covered.See prospective authorization.
Pre-Certification Review
Utilization management performed prior to a patient´s admission, stay, or other service or course of treatment. Also known as Prior Authorization.
Pre-Existing Condition
A health problem that existed before the date your insurance became effective. Each health insurance company uses its own particular definitions of pre-existing condtiion. However, the following statement is in line with most insurance company provisions: "A pre-existing condition is a medical condition that would cause a normally prudent person to seek treatment during the twelve months prior to the beginning of coverage."
Primary Care
General medical care that is provided directly to a patient without referral from another physician. It is focused on preventative care and the treatment of routine injuries and illnesses.
Primary Care Case Manager (PCCM)
In states that have obtained a Section 1915(b) waiver, a primary care provider who contracts directly with the state to provide case management services, such as coordination and delivery of services, to Medicaid patients in an effort to reduce emergency room use, increase preventive care, and improve overall effectiveness by fostering a close physician-patient relationship.
Under a health maintenance organization (HMO) plan, the primary care physician is usually an insured person´s first contact for health care. This is often a family physician, internist, or pediatrician. A primary care physician monitors patient health, treats most patient health problems, and refers patients, if necessary, to specialists. See primary care provider.
Primary Care Provider
A physician or other medical professional who serves as a group member´s first contact with a plan´s Health Care system. Also known as a primary care physician, personal care physician, or personal care provider.
Primary Plan / Insurance
This is the plan that pays first when you are covered by more than one insurance plan.
Primary Source Verification
A process through which an organization validates credentialing information from the organization that originally conferred or issued the credentialing element to the practitioner.
In the context of a pharmacy benefit management (PBM) plan, a program that requires physicians to obtain certification of medical necessity prior to drug dispensing. Also known as a medical-necessity review or pre-certification review.
Prior Qualifying Coverage
Health plan coverage that was in effect before the effective date of the current or new coverage.
Private Duty Nurse
Direct, comprehensive care on an hourly or live-in basis.
A type of Medicare Health Plan in which you may go to any Medicare-approved doctor or hospital that accepts the plan's payment. The insurance plan, rather than the Medicare Program, decides how much it will pay and what you pay for the services you get. You may pay more or less for Medicare-covered benefits. You may have extra benefits Original Medicare doesn't cover.
Private Health Plan
While many people with Medicare get their health coverage from Original Medicare, some people choose to get their benefits from a Medicare private health plan, sometimes called a "Medicare Advantage" plan. These private health plans contract with Medicare and are paid a fixed amount to provide Medicare benefits. They are generally "managed care plans". The most common types are Health Maintenance Organizations (HMO), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPO), and Private Fee-For-Service (PFFS) plans. Also see Medicare Part C.
Process Measures
Health Care quality indicators related to the methods and procedures that a managed care organization and its providers use to furnish care.
Professional Physician Services
Refers to medical service provided by a physician. Or service rendered by a physician or non-physician acting under the supervision, instruction, referral, or prescription of a physician—could also include physician assistant, nurse practitioner, clinical nurse specialist, and physical therapist.
Profiling
Promise Keeping / Truthtelling
An ethical principle which, when applied to managed care, states that managed care organizations and their providers have a duty to present information honestly and are obligated to honor commitments.
PROs
See Peer Review Organizations.
Prospective Authorization
Authorization to deliver Health Care service that is issued before any service is rendered. Also known as precertification.
Prosthetic Device
A device that replaces all or a portion of a part of the human body. These devices are necessary because a part of the body is permanently damaged, is absent or is malfunctioning.
Any person (doctor or nurse) or institution (hospital, clinic, or laboratory) that provides medical care.
Provider Manual
A document that contains information concerning a provider´s rights and responsibilities as part of a network.
Provider Network
That set of providers with which a carrier has contracted to provide services to the Accountable Health Plan´s covered persons. In the case of a "fee-for-service" or non-network Health Benefit Plan, the Provider Network will be deemed to be all licensed providers of covered services.
Provider-Sponsored Organization (PSO)
A Health Care organization established and organized, or operated, by a Health Care provider or a group of affiliated Health Care providers to arrange for the delivery, financing, and administration of Health Care that meets requirements established by the Balanced Budget Act of 1997 and that has the authority to contract directly with Medicare.
PSO
See Provider-Sponsored Organization.
Psychotrophic Drugs
Antidepressants, anti-anxiety drugs, and anti-psychotic drugs used for delusions, extreme agitation, hallucinations, or paranoia. They are often referred to as mind or behavior altering drugs.
Locally based, privately operated organizations that offer affordable group health coverage to businesses with fewer than 100 employees. Also known as purchasing pools, health insurance purchasing co-ops (HPCs), employer purchasing coalitions, or purchasing coalitions.
Purchasing Coalitions
Purchasing Pools
Pure Community Rating
See Standard Community Rating.

Q . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W
QM
QM Committee
MCO committee responsible for oversight of the quality management program including the setting of standards, review of data, feedback to providers, follow-up, and approval of sanctions and for the quality of care delivered to members.
Quality
In a managed care context, an MCO´s success in providing Health Care and other services in such a way that plan members´ needs and expectations are met.
An organization-wide process of measuring and improving the quality of the Health Care provided by an MCO.
Qualified Medicare Beneficiary (QMB)
A Medicaid program for people with Medicare who need help in paying for Medicare services. The person with Medicare must have Medicare Part A and limited income and resources. For those who qualify, the Medicaid program pays Medicare Part A and Part B premiums, and Medicare deductibles and coinsurance amounts for Medicare services.
Quality Program
An organization-wide initiative to measure and improve the service and care provided by an MCO.
Quantity Limit
For safety and cost reasons, plans may limit the quantity of drugs that they cover over a certain period of time. If the drug has a quantity limit restriction, you should contact the plan for more details. If you take one pill per day and the drug has a 30 day/month quantity limit, the impact will be minimal (i.e., you may not be able to refill the prescription until a few days before running out of pills). If you currently take 2 pills per day and the quantity limit is 30 pills per month, you would need to work with the plan to get authorization for the higher quantity.
R . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W
Radiation Therapy
Treatment of disease by x-ray, radium, cobalt or high energy particle sources.
RAF
Rate Spread
The difference between the highest and lowest rates that a health plan charges small groups. The NAIC Small Group Model Act limits a plan´s allowable rate spread to 2 to 1.
Rating
The process of calculating the appropriate premium to charge purchasers, given the degree of risk represented by the individual or group, the expected costs to deliver medical services, and the expected marketability and competitiveness of the MCO´s plan.
RBRVS
See Resource-Based Relative Value Scale.
Reasonable and Customary (R &C) Charge
A term used to refer to the commonly charged or prevailing fees for health services within a geographic area. A fee is generally considered to be reasonable if it falls within the parameters of the average or commonly charged fee for the particular service within that specific community. "Reasonable and Customary (R&C) Charge" essentially means the same thing as "Usual and Customary (U&C) Charge."
Rebate
A reduction in the price of a particular pharmaceutical obtained by a PBM from the pharmaceutical manufacturer.
Recredentialing
Reexamination by an MCO of the qualifications of a provider and verification that the provider still meets the standards for participation in the network.
Referral
An authorization from the primary care physician for the patient to see a specialist or get certain services. In many HMO plans, the insured person needs to get a referral before they get care from anyone except the primary care physician. If the referral is not received, the HMO may cover resulting expenses.
Rehabilitative Care
The care of patients with the intent of curing, improving or preventing a worsening of their condition. For example, physical therapy after a hip replacement surgery to resume walking, or occupational therapy to prevent carpal tunnel syndrome.
Reinstatement
Policies which have lapsed can usually be reinstated by paying the past due premiums and giving appropriate evidence of insurability.
Relative Value of Services
A method used by MCOs of determining provider reimbursement that assigns a weighted value to each medical procedure or service. To determine the amount the MCO will pay to the physician, the weighted value is multiplied by a money multiplier. Also known as a relative value of services.
Renewability
Group health insurance plans are normally 1 year term. Insurers generally review the claims experience of the group at each renewal date and make a renewal offer often at a different premium. The company then decides whether to accept the renewal offer.
Individual policies are renewed periodically (as specified in the policy). Premiums for individual health insurance plans are adjusted based on the experience of all similar individual health insurance plans issued by the insurance company. Details of renewability are spelled out in the policy.
Renewal Underwriting
The process by which an underwriter reviews each year all the selection factors that were considered when the contract was issued, then compares the group´s actual utilization rates to those the MCO predicted to determine the group´s renewal rate.
Report card
A set of performance measures applied uniformly to different health plans or providers.
Rescind
Cancellation of an insurance contract as of the effective date. When a health insurance contract is rescinded, coverage is canceled and all monies are returned - minus any claims paid. This most often occurs when misrepresentations were made to the insurance company at the time of application.
Reserve Days
Reserves
Estimates of money that an insurer needs to pay future business obligations.
Resource-Based Relative Value Scale (RBRVS)
A method used by MCOs of determining provider reimbursement that attempts to take into account, when assigning a weighted value to medical procedures or services, all resources that physicians use in providing care to patients, including physical or procedural, educational, mental (cognitive), and financial resources.
Respiratory Therapy
Treatment of illness or disease that is accomplished by introducing dry or moist gases into the lungs.
Respite Care
Temporary care provided to a terminally ill patient allowing a family member who may be the primary caretaker to take a break from nursing duties. See Hospice Care.
Health insurance provided by employers to former employees who have retired. Retiree insurance always pays secondary to Medicare. Also see supplemental insurance.
Retrospective Authorization
Authorization to deliver Health Care service that is granted after service has been rendered.
Retrospective Review
A review of claims and medical records for medical necessity and appropriateness after the episode of care is concluded and before and/or after the claim is submitted by the provider.
Revenues
The amounts earned from a company´s sales of products and services to its customers.
An amendment to an insurance policy that becomes a part of the insurance contract and expands or limits the benefits payable. Also called an endorsement.
Risk
For a health insurance company, risk is the chance of loss, the degree of probability of loss or the amount of possible loss. For an individual, risk represents such probabilities as the likelihood of surgical complications, medications´ side effects, exposure to infection, or the chance of suffering a medical problem because of a lifestyle or other choice. For example, an individual increases his or her risk of getting cancer if he or she chooses to smoke cigarettes.
The statistical adjustment of outcomes measures to account for risk factors that are independent of the quality of care provided and beyond the control of the plan or provider, such as the patient´s gender and age, the seriousness of the patient´s illness, and any other illnesses the patient might have. Also known as case-mix adjustment.
A Risk Adjustment Factor (RAF) is assigned to each group during underwriting based on an evaluation of the group´s health history. Each group´s final medical rates are determined by multiplying the standard rates by their RAF. A Company uses RAFs from 0.90 to 1.10 for groups of 2-50 and 0.85 to 1.10 for groups of 51-99.For example, If a standard rate is $100 and the RAF is 1.05 ($100 x 1.05), the group´s actual rate would be $105.
Risk Class
A group of insureds who present a substantially similar risk to the insurance company. Among the most common risk classes used by life and health insurance companies are male or female, standard, preferred, nonsmoker, substandard and uninsurable.
Risk Contract
An arrangement in which a health provider offers a range of health services to a group of patients for a pre-paid amount.
RVS
S . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W
Schedule of Benefits and Exclusions
A health insurance listing of the benefits which are covered under the policy guidelines as well as services which are not provided under the policy.
Second Opinion
It is a medical opinion provided by a second physician or medical expert, when one physician provides a diagnosis or recommends surgery to an individual. Individuals are encouraged to obtain second opinions whenever a physician recommends surgery or presents an individual with a serious medical diagnosis.
Second Surgical Opinion
This is an opinion provided by a second physician, when one physician recommends surgery to an individual. Most health insurance policies cover second surgical opinions.
Applies only when you have more than one health insurance plan. The second plan pays only after the primary plan has processed the claim.
Section 1115 Waivers
Waivers that states could obtain from the federal government which allowed them to set up managed care demonstration projects.
Section 1915(b) Waivers
Waivers that states could obtain from the federal government that allowed them to restrict a Medicaid beneficiary´s choice of providers by using a primary care case manager or other arrangement.
Segments
See Market Segments.
Self-Employed Health Insurance
Insurance for the self-employed is often more expensive and more limited, however, similarly to all "small business health insurance", it offers certain tax advantages.
A health plan under which an employer or other group sponsor, rather than an MCO or insurance company, is financially responsible for paying plan expenses, including claims made by group plan members. Also known as a self-insured plan.
Self-Insured
The self-insured employer assumes risk for health care expenses in a plan that is self-administered or administered through a contract with a third-party organization. This form of coverage is regulated by the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974. Hence, self-insured health plans fall under federal, rather than state, regulation. See Self-Funded Plan.
Semiprivate Room
A hospital room that contains two (or more) beds, usually with a curtain separating the beds.
Senior Market
A market segment that is comprised largely of persons over age 65 who are eligible for Medicare benefits.
Service Area
The area where a health plan accepts members. For HMOs, it is also the area where services are provided. A health plan may terminate coverage for persons who move out of the plan´s service area.
Service Quality
An MCO´s success in meeting the nonclinical customer service needs and expectations of plan members.
A federal act which established as national policy the concept of a competitive marketing system by prohibiting companies from attempting to (1) monopolize any part of trade or commerce or (2) engage in contracts, combinations, or conspiracies in restraint of trade. The Act applies to all companies engaged in interstate commerce and to all companies engaged in foreign commerce. See also antitrust laws.
SHIP (State Health Insurance Assistance Program)
A federally funded program that answers questions about Medicare, free of charge.
An injury or illness that keeps a person from working for a short time. The definition of short-term disability (and the time period over which coverage extends) differs among insurance companies and employers. Short-term disability insurance coverage is designed to protect an individual´s full or partial wages during a time of injury or illness (that is not work-related) that would prohibit the individual from working.
Short Term Health / Medical Insurance (Click here for a quote).
Temporary health coverage for an individual for a short period of time, usually from 30 days to six months.
Medically-necessary care provided by a nurse or trained medical staff.
A licensed institution that provides regular medical care and treatment to sick and injured persons. Daily medical records are kept and patients are under the care of a licensed physician.
Skilled Nursing Services
Services from a registered nurse, which include administration of medications; tube feedings; catheter changes; wound care; teaching and training activities; observation and assessment of a patient's condition; and management and evaluation of a patient's plan of care.
Small Business Health Insurance (Click here for a quote).
Although each MCO´s size limit may vary, generally a group composed of 2 to 50 members for which health coverage is provided by the group sponsor. See Group Health Plan.
Small Group (Click here for a quote).
Although each MCO´s size limit may vary, generally a group composed of 2 to 50 members for which health coverage is provided by the group sponsor. See Group Health Plan.
SNP
Social Security Administration (SSA)
The United States government agency responsible for advancing the economic security of Americans through shaping and managing various programs, including Medicare, Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI), Supplemental Security Income (SSI) and Extra Help.
Special Benefit Networks
Provider networks for particular services, such as mental health, substance abuse, or prescription drugs.
Special Election Period
A period of time during which you can change your Medicare Advantage plan or choose to re-enroll in Original Medicare. You can make this change if you move outside your current plan´s service area, if your plan provider does not renew its contract with the federal government, and in other special circumstances determined by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. The Special Election Period is different from the Special Enrollment Period.
Special Enrollment Period (SEP)
A period of time during which you can enroll in Medicare Part B other than the Initial Enrollment Period. The main reason not to enroll during the Initial Enrollment Period is because you were covered under an existing group plan provided by an employer. The Special Enrollment Period lasts for 8 months after your group coverage or your employment ends, whichever comes first.
A Special Needs Plan (SNP) is a Medicare Advantage plan (private health plan) that exclusively serves at least one of the following groups:
When completing the SNP proposal application, MA organizations can choose to offer a C-SNP that targets any one of the groups below:
- Dual Eligible SNP: You must be eligible for Medicare and Medicaid (in California this is known as Medi-Cal) to enroll in a Dual Eligible Special Needs Plan. Premiums, copays, coinsurance, and deductibles may vary based on the level of Extra Help that beneficiaries may receive, and the beneficiary should contact the plan for further details.
- Chronic SNP: To enroll in a Chronic Special Needs Plan, you must meet and retain the following eligibility requirements: have Medicare (Part A and B) and have Congestive Heart Failure (CHF).
- Institutional SNP: Institutionalized beneficiaries
CMS will accept proposals with the following multi-condition groupings:
- A single CMS-approved chronic condition;
- A CMS-approved group of multiple chronic conditions; or
- An MA organization-customized grouping of multiple chronic conditions selected from the 15 CMS-approved SNP-specific chronic conditions.
For MA organizations that are approved to offer a C-SNP targeting one of the above-listed groups, beneficiaries need only to have one of the qualifying conditions for enrollment.
- Group 1: Diabetes mellitus and chronic heart failure
- Group 2: Chronic heart failure and cardiovascular disorders
- Group 3: Diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disorders
- Group 4: Diabetes mellitus, chronic heart failure, and cardiovascular disorders
- Group 5: Stroke and cardiovascular disorders
Social Security Administration (SSA)
The United States government agency responsible for advancing the economic security of Americans through shaping and managing various programs, including Medicare, Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI), Supplemental Security Income (SSI) and Extra Help.
Special Benefit Networks
Provider networks for particular services, such as mental health, substance abuse, or prescription drugs.
Special Election Period
A period of time during which you can change your Medicare Advantage plan or choose to re-enroll in Original Medicare. You can make this change if you move outside your current plan´s service area, if your plan provider does not renew its contract with the federal government, and in other special circumstances determined by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. The Special Election Period is different from the Special Enrollment Period.
Special Enrollment Period (SEP)
A period of time during which you can enroll in Medicare Part B other than the Initial Enrollment Period. The main reason not to enroll during the Initial Enrollment Period is because you were covered under an existing group plan provided by an employer. The Special Enrollment Period lasts for 8 months after your group coverage or your employment ends, whichever comes first.
Specialist
A physician who practices medicine in a specialty area. Cardiologists, orthopedists, gynecologists and surgeons are all examples of specialists. Under most health plans, family practice physicians, pediatricians and internal medicine physicians are not considered specialists. Some health plans require preauthorization from your primary care physician before you can see a specialist.
Specialty Health Maintenance Organization (specialty HMO)
An organization that uses an HMO model to provide Health Care services in a subset or single specialty of medical care.
Specialty HMO
See Specialty Health Maintenance Organization.
Specialty Services
Services that are provided by independent, specialty organizations rather than by the MCO providing the basic health plan.
Specific Disease Policy
A plan that covers expenses only for a specific disease identified in the policy. Also called Dread Disease policy.
Specific Stop-Loss Coverage
See Individual Stop-Loss Coverage.
Speech Therapy
Treatment or the correction of a speech impairment that resulted from birth, or from disease, injury or prior medical treatment.
SSDI (Social Security Disability Insurance)
Monthly benefits provided through the Social Security Administration for people who lose their ability to work because of a severe medical impairment disability. People who receive SSDI for 24 months are eligible for Medicare.
SSI (Supplementary Security Income)
Monthly benefits provided through the Social Security Administration for people with low incomes and assets who are 65 or older, blind, or have a disability.
Staff Model
Staff model is a type of HMO in which care is provided by physicians who are employees of the HMO. This contrasts with the "independent practice association (IPA)" HMO, in which independent physicians contract with the HMO.
A type of community rating in which an MCO considers only community-wide data and establishes the same financial performance goals for all risk classes. Also known as pure community rating.
Standard of Care
A diagnostic and treatment process that a clinician should follow for a certain type of patient, illness, or clinical circumstance.
Stark Laws
See Ethics in Patient Referrals Act.
State Insurance Department
An administrative agency that implements state insurance laws and supervises (within the scope of these laws) the activities of insurance companies operating within the state.
State-Mandated Benefits
Benefits for a variety of medical conditions that a given state requires of health insurance policies sold in that state.
Statutory Solvency
An insurer´s ability to maintain at least the minimum amount of capital and surplus specified by state insurance regulators.
Step Therapy
In some cases, plans require you to first try one drug to treat your medical condition before they will cover another drug for that condition. For example, if Drug A and Drug B both treat your medical condition, a plan may require your doctor to prescribe Drug A first. If Drug A does not work for you, then the plan will cover Drug B. If a drug has step therapy restrictions, you will need to work with the plan and your doctor to obtain an exception.
Stop-Loss Insurance
A type of insurance coverage that enables provider organizations or self-funded groups to place a dollar limit on their liability for paying claims and requires the insurer issuing the insurance to reimburse the insured organization for claims paid in excess of a specified yearly maximum.
Stop-Loss Provision
The point when the insurance company will begin to pay 100% of accrued medical expenses.
Structural Integration
The unification of previously separate providers under common ownership or control.
Structure Measures
Health Care quality indicators related to the nature and quality of the resources that a managed care organization has available for patient care.
Subauthorization
The authorization of one Health Care service concurrently with the authorization of another service. For example, an authorization for hospitalization may cover surgery, anesthesia, pathology, and radiology performed during the hospitalization.
Subscriber
The individual in whose name a contract is issued or the employee covered under an employer´s group health contract. See Insured.
Subsidiary
A company that is owned by another company, its parent.
Substance Abuse / Chemical Dependency
Conditions that include, but are not limited to (1) psychoactive substance induced mental disorders; (2) psychoactive substance use dependence; and (3) psychoactive substance use abuse. Chemical dependency does not include addition to or dependency on, tobacco or food substances (or dependency on items not ingested).
Fills gaps in Original Medicare coverage by helping to pay for the portion of health care expenses that Original Medicare does not pay for, such as deductibles and coinsurances. Supplemental insurance includes Medigap plans and retiree insurance from a former employer. Supplemental insurance may offer additional benefits that Original Medicare does not cover. See also, Secondary Insurance.
Supplier
A person or company from whom you can buy medical equipment, like a walker or wheelchair. See Durable Medical Equipment.
Surplus
The amount that remains when an insurer subtracts its liabilities and capital from its assets.
Apply Online for Dental & Vision Coverage
T . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W
Terminal Illness
A disease or condition that cannot be cured or adequately treated, and is expected to result in eventual death.
Termination Provision
A provider contract clause that describes how and under what circumstances the parties may end the contract.
Termination with Cause
A contract provision, included in all standard provider contracts, that allows either the MCO or the provider to terminate the contract when the other party does not live up to its contractual obligations.
Termination without Cause
A contract provision that allows either the MCO or the provider to terminate the contract without providing a reason or offering an appeals process.
Therapeutic Substitution
The dispensing of a different chemical entity within the same drug class of a drug listed on a pharmacy benefit management plan´s formulary. Therapeutic substitution always requires physician approval.
Third Party Administrator (TPA)
A company that provides administrative services to MCOs or self-funded health plans.
Any payer of health care services other than the insured person. This can be an insurance company, HMO, PPO, or the federal government.
Tiers, Drug
See Drug Tiers.
TPA
See Third Party Administrator.
Traditional Medicare
Travel Health Insurance (Click here for a quote).
This insurance is purchased to provide you with coverage when you´re traveling abroad.
Treatment Codes
See Diagnostic and Treatment Codes.
A Health Care plan, available to more than 6 million military personnel and their families, which is administered by private contractors who are selected for participation through a competitive procurement process. TRICARE offers members three plan options: TRICARE Prime (a capitated HMO with nominal premiums and copayments), TRICARE Extra (a PPO with standard CHAMPUS deductibles), and TRICARE Standard (the current fee-for-service CHAMPUS plan with provider choice and no premiums). See also Civilian Health and Medical Program of the Uniformed Services.
Triple-Option
Insurance plans that offer three options from which an individual may choose. Usually, the three options are: traditional indemnity, an HMO, and a PPO.
Types of Health Insurance Plans
- An PPO (Preferred Provider Organization) is a similar organization in that some health care providers are contracted to provide health care services at contracted rates, but it offers more flexibility, since most HMOs require that their members stay within their provider network. When you receive care from in-network doctors, you will save money. But you will also have coverage with any physician or specialist - even if they are not in the preferred network.
- An HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) is one one of the most affordable health plans available. You must go to doctors within the network and choose a primary care physician. However the health-care providers have contracted with the insurance company to provide health-care services at fixed rates. So they usually don't require members to satisfy a deductible before benefits take effect, and most services are covered by set, lower cost co-payments.
- An POS (Point of Service) is an "HMO/PPO" hybrid; sometimes referred to as an "open-ended" HMO when offered by an HMO. POS plans resemble HMOs for in-network services. Services received outside of the network are usually reimbursed in a manner similar to conventional indemnity plans (e.g., provider reimbursement based on a fee schedule or usual, customary and reasonable charges).
- An EPO (Exclusive Provider Organization) is a health care benefit arrangement that is similar to a preferred provider organization in administration, structure, and operation, but which does not cover out-of-network care. An EPO is a type of health plan that utilizes primary care physicians to coordinate access to in-network medical services for plan participants. EPOs feature financial incentives to seek health care services from in-network providers, and patients are responsible for considerable out-of-pocket expenses if they receive care from out-of-network providers without authorized referrals. EPO providers are only paid for services provided (HMOs receive monthly payments from carriers); and the premiums for EPOs are generally cheaper than HMOs. EPOs are structurally similar to PPOs, but EPO members cannot file claims for non-network office visits, which PPO and POS plans allow.
- An HSA (Health Savings Account) offers maximum cost effectiveness for your benefits plan. It gives your employees an account called a Health Savings Account, or HSA, which they can use to pay for their medical care and prescriptions. The HSA is funded by a your pre-tax contributions. It also includes a Traditional Health Coverage (PPO) component, similar to a typical health plan, to help protect you against large health expenses.
U . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W
UC&R Fee
See Usual, Customary, and Reasonable Fee.
UM
Underwriter
- The person who assesses and classifies the potential degree of risk that a proposed insured represents.
- The person or organization that guarantees that money will be available to pay for losses that are insured against. In this sense, the insurance company is the underwriter.
The process of assessing and classifying the potential degree of risk that a proposed insured represents. Also called selection of risks.so that the appropriate rates may be assigned. The process also includes rejection of those risks that do not qualify.
Underwriting Department
The department in a life and health insurance company that selects the risks that the company will insure. The underwriting department tries to make sure that the actual mortality or morbidity rates of the company's insureds do not exceed the rates assumed when premium rates were calculated. The underwriter considers an applicant's age, weight, physical condition, personal and family medical history, occupation, financial resources, and other selection factors to determine the degree of risk represented by the proposed insured. This department also participates in the negotiation and management of reinsurance agreements, through which an insurance company transfers some or all of an insurance risk to another insurance company. Also called the new business department.
Underwriting Impairments
Factors that tend to increase an individual´s risk above that which is normal for his or her age.
Underwriting Manual
A summary of the methods used by a particular insurer to evaluate and rate risks. The underwriting manual provides underwriters with background information on underwriting impairments and serves as a guide to suggested underwriting actions when various impairments are present. See also risk class.
Underwriting Requirements
Printed instructions that indicate what evidence of insurability is required for a given situation and which of several optional information sources will be needed to provide underwriters with necessary information. Sources of information may include medical records and the results of physical examinations. Underwriting requirements are graduated based on the proposed insured's age and the amount of coverage requested.
Unearned Income
Money you get from sources other than current employment. Includes Social Security benefits, Veterans benefits, pensions, annuities and other regular payments you receive, such as alimony and workers' compensation.
Uninsurable Risk Class
The group of people with a risk of loss so great that an insurance company will not offer them insurance.
UR
Urgent Care
The services received for a sudden, serious, or unexpected illness, injury or condition, other than one which is life threatening, that requires immediate care for the relief of severe pain or diagnosis and treatment of such condition.
URO
See Utilization Review Organization.
Usual, Customary and Reasonable (UC&R) Fee
Charges represent the average or most common amount charged by providers for a particular service, treatment, or supply in the same geographic area. Typically information on rates for procedures is compiled into a data bank and updated periodically. So when a claim is submitted for a plan with UC&R benefits, the insurance company before making the claim payment reviews the UC&R rate and double checks that hospitals and doctors are not billing excessively for the particular service or procedure.
Managing the use of medical services to ensure that a patient receives necessary, appropriate, high-quality care in a cost-effective manner.
The evaluation of the medical necessity, efficiency, and/or appropriateness of Health Care services and treatment plans.
Utilization Review Committee
Committee that reviews utilization issues brought to it by the medical director, often approving or reviewing policy regarding coverage, reviewing utilization patterns of providers, and approving or reviewing the sanctioning process against providers.
Utilization Review Organization (URO)
External reviewers who assess the medical appropriateness of suggested courses of treatment for patients, thereby providing the patient and the purchaser increased assurance of the appropriateness, value, and quality of Health Care services.
V . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W
Valid Waivers are those individuals who have other health care coverage through a spouse, parent or legal guardian, individual coverage, coverage through another employer of coverage provided through a government subsidized health care program.
Variances
The differences obtained from subtracting actual results from expected or budgeted results.
Veterans Administration (VA) Benefits
Benefits given by the federal government to people who have been in “active” service in the military, naval, or air service (veterans, not career officials) and, under certain conditions, to their family members. These benefits include pensions, educational stipends and health care, among others. Veterans can receive VA health care services only at VA facilities.
W . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W
Waiver
See Valid Waivers.
Waiver of Coverage
A section on the enrollment form which states that an employee was offered insurance coverage but opted to waive this coverage.
Waiting Period
A period of time when the health plan does not cover a person for a particular health problem.
Well-Baby Care
Preventative health services, including immunizations, for young children within an age range specified by the health plan. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends well child visits at the following times:
- Before birth (for first-time parents).
- Before your newborn is discharged from the hospital. If your baby is discharged before two full days of life, your baby should be seen again within 48 and 72 hours.
- During the first year of life - a visit at about 2-4 weeks of age and at 2, 4, 6, 9, and 12 months of age.
- During the second year of life - visits at 15, 18, and 24 months of age.
- In early childhood - yearly visits from 2-5 years of age.
- During early school years - visits at 6, 8, and 10 years of age.
- In adolescence and early adulthood - yearly visits from 11-21 years of age.
Wellness Office Visit
A physician´s office visit which is not prompted by sickness or injury.
Wellness Program
A health management program that incorporates the components of disease prevention, medical self-care, and health promotion. It utilizes proven health behavior techniques that focus on preventive illness and disability, which respond positively to lifestyle related interventions. Programs are designed to integrate with existing health care benefits; e.g., flex benefits, HMO, PPO; support the reduction in the demand for health care resources; and address the issues of dependent coverage and services for high-risk employees.
Withhold
A percentage of a provider´s payment that is "held back" during the plan year to offset or pay for any cost overruns for referral or hospital services. Any part of the withhold not used for these purposes is distributed to providers.
Work Credits
The unit of measurement that determines when you are eligible to receive Social Security benefits, including Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI). How many work credits you earn during a year (up to a maximum of four) depends on how much money you make during that year. The Social Security Administration (SSA) determines the amount that you must earn to receive one work credit.
Workers Compensation
A state-mandated insurance program that provides benefits for Health Care costs and lost wages to qualified employees and their dependents if an employee suffers a work-related injury or disease.
 Apply Online for Dental & Vision Coverage Apply Online for Dental & Vision Coverage
|
Barricks Insurance ServicesImportant Disclaimer: Answers and comments provided above are general information, and are not intended to substitute for informed professional medical, psychiatric, psychological, tax, legal, investment, accounting, governmental, or other professional advice. We do not endorse, and expressly disclaims liability for any product, manufacturer, distributor, service, health plan, or service provider mentioned or any opinion expressed in the website. Replies, comments, or information gathered on Barricks.com website may not be accurate but are intended to be helpful.