
Glossary of Life Insurance Terms
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
To search this Glossary, press Ctrl & F and type the word you wish to find into the box.
A . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
Absolute Assignment
An irrevocable transfer of complete ownership of a life insurance policy from one party to another. See also assignment.
Some companies provide "accelerated benefits," also known as "living benefits." This rider allows you, under certain circumstances, to receive the proceeds of your life insurance policy before you die. Such circumstances include terminal or catastrophic illness, the need for long-term care, or confinement to a nursing home. Ask your agent for information about these and other policy riders.
Accelerated Death Benefits
This benefit advances up to 50% of the death benefit to an insured, while living, if diagnosed with a terminal condition with 12 months or less to live.
Accumulation Value
The cash accumulation component of an annuity, universal life insurance policy or variable life insurance policy. The accumulation value reflects premiums received, withdrawals made, expenses charged, cost of insurance deducted and interest credited.
ACLI
See American Council of Life Insurance.
Accidental Death and Dismemberment (AD&D) Rider
A supplementary benefit rider or endorsement that provides for an amount of money in addition to the basic death benefit of a life insurance policy. This additional amount is payable only if the insured dies or loses any two limbs or the sight of both eyes as the result of an accident. Some AD&D riders pay one half of the benefit amount if the insured loses one limb or the sight in one eye.
Accidental Death Benefit (ADB) Rider
A supplementary benefit rider or endorsement that provides for an amount of money in addition to the basic death benefit of a life insurance policy. This additional amount is payable only if the insured dies as the result of an accident.
Accumulation Phase
The phase during which the annuity owner makes payments into the contract and accumulates earnings.
Actively-at-Work Pprovision
A provision found in many group insurance contracts which specifies that, if an employee is absent from work because of sickness, injury, or certain other specified reasons, on the day the employee´s coverage under the contract is due to begin, then coverage will not begin until the day the employee returns to work.
Actuarial Department
The department in a life and health insurance company responsible for seeing that the company´s operations are conducted on a mathematically sound basis. In conjunction with other departments, it designs and revises a company´s life and health insurance products. The actuarial department calculates premium and dividend rates, determines what a company´s reserve liabilities should be, and establishes nonforfeiture, surrender, and loan values. It also does the research needed to predict mortality and morbidity rates, to establish guidelines for selecting risks, and to determine the profitability of the company´s products.
Actuary
A technical expert in life insurance, particularly in mathematics. A person in this job applies the theory of probability to calculate mortality rates, morbidity rates, lapse rates, premium rates, policy reserves, and other values.
ADB rider
AD&D Rider
See Accidental Death and Dismemberment.
Administrative Services Oonly (ASO)
An arrangement whereby an organization (usually an employer) hires an outside firm to perform specific administrative services, usually including claim administration, for a group health insurance program. The organization retains financial responsibility for paying claims. See also self-insured group insurance and third-party administrator (TPA).
Age at Issue
The insured´s age at the time coverage takes effect. Insurance plans typically define issue age as either the age at the insured´s last birthday or nearest birthday.
Age Discrimination in Employment Act of 1967 (ADEA)
Legislation that protects employment rights of individuals age 40 and over. ADEA prohibits age-based firings and generally prevents employers from forcing employees to retire at age 65. In relation to pension plans, ADEA prohibits employers from discontinuing contributions or benefit accruals to an individual´s pension plan after that person reaches age 65.
Agent of Record (Agent)
The Agent or Broker who is recognized by the insurer as the person to whom the commission is to be paid. An authorized representative of an insurance company who solicits and services insurance contracts.
Agent´s Statement
The portion of the insurance application in which the agent reports anything he or she knows or suspects about the proposed insured that is not reported by the applicant or proposed insured.
American Council of Life Insurance (ACLI)
An organization which collects and disseminates data on life insurance markets.
Anniversary Date
The annual recurrence of the insurance policy´s effective date. Some policy options that may be exercised may be tied to the anniversary date.
Annual Point to Point Crediting Method
A fixed index annuity crediting method that takes the starting point and ending point of a contract year, disregarding fluctuations in between. If the result is positive, interest will be credited to the contract. If negative, the contract will not earn any interest.
Annual Return
The percentage increase in the value of an investment during a 12-month period or a series of 12-month periods, taking into account compounding of investment dividends or capital gains.
Annuitant
The individual whose lifetime is used to calculate the pay period of a life annuity.
Annuitization
To select a settlement option beginning periodic payments from an annuity contract.
Annuity
A contract issued by an insurance company where guaranteed or variable periodic payments begin at a specified time.
Annuity Starting Date
The date when an annuity contract begins to make periodic benefit payments; the beginning of the payout period.
Antiselection
The tendency of people with a greater-than-average likelihood of loss to apply for or continue insurance to a greater extent than do other people. Also called adverse selection or selection against the insurer.
Applicant
The party applying for an insurance policy.
Application
A form that must be completed by an individual or other party who is seeking insurance coverage. This form provides the insurance company with much of the information it will need to decide whether to accept or reject the risk.
APS
See Attending Physician´s Statement.
ASO
See Administrative Services Oonly.
Asset
Any item of economic value owned by an individual or corporation. Usually refers to items that can be sold and converted to cash. Examples are cash, securities, financial accounts, a house, a car, jewelry and other property.
Asset Allocation
The process of dividing investor funds among several classes of investments to coincide with the investor´s goals, investment period and tolerance for risk. Investments with the highest potential return often have correspondingly high risk of loss. Conversely, investments offering the lowest risk usually have the lowest returns. By allocating assets among different classes of assets the investor seeks to maximize return while managing the associated risk within the comfort level of the investor.
Assignee
The party to whom all or certain contractual rights are transferred under an absolute or collateral assignment.
Assignment
- The transfer of ownership rights in a life insurance policy or other type of contract from one party to another.
- The document that causes the transfer of ownership rights to go into effect. See also absolute assignment and collateral assignment.
Assignment of Benefits
An authorization directing an insurer to make payment directly to a provider of benefits, such as a physician or dentist, rather than to the insured.
Assignor
The person or party who transfers certain contractual rights under an absolute or collateral assignment.
Association Group Insurance
Group insurance extended to the members of a trade, professional, or other association.
Attained Age
The current age of the insured. The age of the insured at the time the insured´s policy was issued plus the number of years elapsed since the policy was issued.
Attending Physician´s Statement (APS)
A written statement from a physician who has treated, or is currently treating, a proposed insured or an insured for one or more conditions. The statement provides the insurance company with information relevant to underwriting a risk or settling a claim.
An optional rider in a universal life contract that provides scheduled increases in face amount based on a designated percentage, beginning in a designated policy year. This option must be applied for at the time of issue of the base policy. You will usually be charged an additional premium.
Automatic Premium Loan Provision
If invoked, an option that allows the insurer to automatically borrow money from a policy´s cash or accumulation value to pay any premium in default at the end of a grace period in order to keep the policy from lapsing.
Automatic Premium Payment
An option that allows the insurer to automatically withdraw money from a policy’s accumulation value to pay a due premium. The option is available only for certain Excess Interest Whole Life plans, and is limited to the excess values only. Excess values are those in excess of the guaranteed cash values.
Aviation Exclusion
A life insurance contract provision which specifies that the death benefit is not payable if the insured dies as a result of certain aviation activities.
B . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
bailout provision
Clause found in an Annuity contract that enables the owner of that contract to withdraw his or her money without surrender penalties, if the annual interest rate is lowered below a certain predetermined minimum.
An arrangement by which a policy owner allows a bank to withdraw money from his or her account on a scheduled basis and transfer the money to an insurance company to be applied as payment to a policy. Also known as an Electronic Funds Transfer.
basic death benefit
The death benefit according to the terms of the original, basic contract of a life insurance policy. The basic death benefit does not include the benefit for any supplementary riders, such as an accidental death benefit (ADB) rider. For policies whose death benefit remains constant, the basic death benefit is equivalent to the face amount. Compare to death benefit and policy proceeds.
beneficiary
The person or other party designated to receive life insurance policy proceeds. See also contingent beneficiary, irrevocable beneficiary, primary beneficiary, and revocable beneficiary.
benefit
The amount of money paid when an insurance claim is approved. Also called the policy benefit.
benefit schedule
Under a group insurance plan, a table or schedule which specifies the amount of coverage provided for each class of insured. Insureds are often classified with reference either to earnings or to rank or position. Also known as schedule of benefits.
blended rates
Group mortality rates that are based partially on a group´s own experience and partially on manual rates. Blended rates are used to determine the appropriate group insurance premium rates for intermediate-size groups. See also experience rating and manual rates.
- An insurance salesperson (agent) who sells insurance products for more than one insurance company.
- For a career agent, to submit insurance applications to companies other than the agent´s own company.
buy-sell agreement
A buy-sell agreement is a contract that provides for the future sale of your business interest or for your purchase of a co-owner´s interest in the business. Buy-sell agreements are also known as business continuation agreements, stock purchase agreements, and buyout agreements.

C . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
capitalization of loan interest
Activity related to loan interest charged or reversed for a policy loan. It is the interest charged for a new loan, or for the interest added to the loan for each policy anniversary. It´s the unearned interest reversed whenever the loan is paid off or a loan payment is applied.
cash equivalents
Investments that are highly liquid and safe, and considered equal to cash. Examples are treasury bills, money market funds and short-term CDs and bonds (maturities of six months or less).
cash value/cash surrender value
The amount that is available in cash for loans and/or withdrawals. Accessing cash surrender value may reduce the death benefit and may increase the risk of lapse. Withdrawals may be subject to surrender charges and could have a permanent effect on the cash value. Loans reduce the cash value and death benefit by the amount of the loan outstanding plus interest. If the policy is surrendered, the cash surrender value is paid to the policy owner.
cash value life insurance
Policy that generates a savings element. Cash values are critical to a permanent life insurance policy. The size of a cash value buildup differs substantially from company to company.
certificate of insurance
A document given to each person insured by a group insurance plan. This document shows the type and amount of coverage to which the group member is entitled and the beneficiary of the coverage. The certificate may also contain a summary of the contract terms as they affect individual group members. See also master contract.
children´s term insurance rider
This rider provides term insurance on each covered child, payable if the child dies before the expiration of his or her coverage (the child attaining age 25 or the policy anniversary on which the primary insured is age 65, if earlier). If the primary insured dies while this rider is in force, a supplementary paid-up policy will be issued on each covered child. This rider is convertible between the child´s ages of 21 - 25 for up to 5 times the face amount of the rider without evidence of insurability. Also known as Children´s Insurance Benefit.
claim
A request for payment under the terms of an insurance policy.
claim administration department
The department in a life and health insurance company responsible for processing claims. In this department, claim examiners review claims presented by policyowners or beneficiaries, verify the validity of claims, and authorize the payment of benefits to the proper person.
claimant
The person or party making a formal request for payment of benefits due under the terms of an insurance contract.
claim examiner
An employee of an insurance company whose responsibilities include investigating claims, approving the claims that are valid, and denying those that are invalid or fraudulent.
claim investigation
The process of obtaining necessary claim information in order to decide whether or not to pay a claim.
claim reserve
A claim department´s estimate of the amount of money needed to pay a claim. The estimate is made with the help of information that the claim department gathers in the course of handling the claim. This information may involve, for example, the extent to which the claim is covered by the policy, the effect of previously paid claims on the amount of coverage available to pay a current claim, and the effect of any applicable reinsurance coverage on the claim.
class beneficiary designation
A beneficiary designation that names several people as a group -- for example, "children of the insured" -- rather than naming each person individually.
COLA
See cost-of-living adjustment.
collateral assignment
A transfer of some ownership rights in a contract from one party to another, generally for a temporary period. Insurance policies are often assigned as collateral for a loan, in which case all transferred rights revert to the assignor when the loan is repaid. See also assignment.
combination company
A life and health insurance company that sells both industrial and ordinary insurance products.
combination clause
A clause in a disability income contract that specifies a point at which the definition of total disability will no longer be based on an insured´s inability to perform his or her "own occupation" but on the insured´s inability to perform "any occupation."
commission
The amount of money paid to an insurance agent for selling an insurance policy. A commission is almost always calculated as a percentage of the premium.
common accident provision
- A provision of many medical expense insurance contracts which specifies that, if two or more members of the same family are injured in the same accident, their combined medical expenses will only be subject to one deductible.
- A provision found in many voluntary group accidental death and dismemberment plans which specifies that the amount payable by the insurance company is limited to a stipulated maximum for all employees killed or injured in a single accident.
common disaster
A situation in which the insured and the beneficiary appear to die simultaneously with no clear evidence of who died first.
common disaster clause
A life insurance policy provision which states that the primary beneficiary must survive the insured by a specified period, such as 60 or 90 days, in order to receive the policy proceeds. Otherwise, the policy proceeds will be paid as though the primary beneficiary had died before the insured.
contestable clause
contestability period
The period of time (usually two years) during which an insurer may challenge the validity of a life insurance policy. See also incontestable clause.
contingent beneficiary
The party designated to receive life insurance policy proceeds if the primary beneficiary should die before the person whose life is insured. Also called the secondary beneficiary or the successor beneficiary.
contract
See policy.
contributory group insurance
Any group insurance plan that calls for the insureds to pay a portion of the cost of the group insurance coverage. Contrast to noncontributory group insurance.
conversion
conversion period
The period of time during which the owner of a term life insurance policy may convert it to another life insurance policy without evidence of insurability.
- The right of a person who is covered by a group insurance policy to convert his or her group coverage to coverage under an individual insurance policy. Such a conversion can be made when a person leaves the group, benefits are downgraded or terminated for a specific class, or when the group master policy is ended.
- The right to change insurance coverage in certain prescribed situations from one type of policy to another. For example, the right to change from an individual term insurance policy to an individual whole life insurance policy.
convertible
See convertible term insurance.
A type of term insurance that allows the policyowner to change the term insurance policy to a whole life policy without providing evidence of insurability. The premium rate is normally based on the age of the insured at the time of the conversion.
cost of insurance
A universal life insurance policy contract provision; the "cost of insurance" is the amount deducted monthly from the accumulation value to cover the pure insurance protection provided by the policy. The amount deducted is calculated based on a number of factors such as age, premium class and net amount at risk.
cost-of-living adjustment (COLA)
An increase in a pension benefit, disability income benefit or life income benefit to compensate for an increase in the cost of living. See also indexation.
credibility percentage
The amount of credit or weight given to a group´s actual claims experience in determining a projection of future claims or in the calculation of a dividend. Sometimes called the credibility factor. See also experience rating and experience refund.
customer service department
The department in a life and health insurance company that is charged with providing assistance to the company´s policyowners, agents, and beneficiaries. Customer service specialists answer policyowners´ requests for information, help them interpret policy language, answer questions about policy coverage, and make changes requested by the policyowner, such as changing the policyowner´s address, beneficiary designation, and mode of premium payment. The customer service department may also send premium notices to customers, collect premium payments, and calculate and process policy loans, nonforfeiture options, dividends, and surrenders. In some companies, the customer service department also processes commission payments for company agents. Also called the client service department, the policy administration department, the policyowner service department, and the service and claim department.
D . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
date of issue
The effective date of the policy or contract as issued by the insurer.
death benefit
The amount of money paid or due to be paid when a person insured under a life insurance policy dies. This amount does not include adjustments for outstanding policy loans, dividends, paid-up additions, or late premium payments. See also basic death benefit and policy proceeds.
death claim
A request for payment under the terms of a life insurance policy.
deferred annuity
A type of annuity contract that delays payments of income, installments or a lump sum until the investor elects to receive them. This type of annuity has two main phases, the savings phase in which you invest money into the account, and the income phase in which the plan is converted into an annuity and payments are received.
dependent life insurance
Group life insurance made available to group members, usually on an optional and contributory basis, to cover the spouse, children, or other dependents of the group member. It is usually sold in small amounts which are intended to pay funeral expenses.
disability
Inability to work due to an injury or sickness. See also partial disability, presumptive disability, and total disability.
disability benefits
Benefits that are payable periodically while an insured continues to be disabled. "Being disabled" is generally defined in terms of inability to work. See also total disability.
disability income insurance
A type of health insurance designed to compensate insured people for a portion of the income they lose because of a disabling injury or illness. Generally, benefits for disability income insurance are provided for the disabled person in the form of monthly payments. Sometimes called loss of time insurance. See also long-term disability income insurance and short-term disability income insurance.
dividend
A return of part of the premium on participating insurance that is based on the insurer´s investment, mortality and expense experience. Dividends are not guaranteed.
double indemnity
Death benefit coverage that pays an additional benefit equal to the basic death benefit of the policy if the insured´s death is accidental. See also accidental death benefit (ADB) rider.
E . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
E&O insurance
Electronic Funds Transfer
See Bank Draft.
eligibility period
In contributory group insurance plans, the period of time, usually 31 days, during which a new employee may apply for group insurance coverage.
eligibility requirements
The conditions a person must meet in order to be a participant in a group life insurance, group health insurance, or retirement plan.
elimination period
See waiting period.
emergency fund
An emergency fund is money set aside to allow you to weather any unexpected events or expenses in your life. Emergency funds are often used to pay for expenses not incorporated into the budget such as property losses or medical expenses not covered by insurance, or living expenses during a period of unemployment. It is generally recommended that your emergency fund equal three to six months of your living expenses.
Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 (ERISA)
A federal law establishing:
ERISA also established the Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation (PBGC).
- the rights of pension plan participants,
- standards for the investment of pension plan assets, and
- requirements for the disclosure of plan provisions and funding.
endorsement
See rider.
endow
The point in time when a life insurance policy´s cash value equals the face amount.
error and omissions (E&O) insurance
Insurance designed to cover claims that result from the negligent acts or mistakes of an agent, including:
- his or her vicarious liability stemming from negligent acts or...
- mistakes committed by individuals for whom the agent is legally liable.
estate planning
The process of planning for the efficient transfer of assets at one´s death. Estate planning begins with preparing a will and may also include naming a power of attorney, establishing trusts and making pre-death gifts. For high net worth individuals, it may also include estate and gift tax planning.
estate tax
Tax imposed by a state or the federal government on the transfer of property from a deceased to his/her heirs.
evidence of insurability
Proof that a person is an insurable risk.
excess interest
Amount credited to the cash value of an insured´s life insurance policy above the minimum interest rate it guarantees. This payment is of extreme importance to a policyowner since it will directly affect the size of the cash value. See also Cash Value Life Insurance.
exclusions
Specific conditions or circumstances for which the policy will not provide benefits.
executor
An individual or institution that is tasked with the settling of an estate for the deceased. Activities may include gathering the assets, paying the taxes and distributing the estate in accordance with the will.
expected return
The amount expected to be received by an annuitant under an annuity contract, based on the periodic payment and the annuitant´s life expectancy or the guaranteed number of payments, as calculated when benefits begin. The expected return is utilized to calculate federal income tax of interest received in each annuity payment.
The average of a probability distribution of possible returns, calculated by using the following formula:
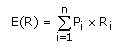
How do you calculate the average of a probability distribution? As denoted by the above formula, simply take the probability of each possible return outcome and multiply it by the return outcome itself. For example, if you knew a given investment had a 50% chance of earning a 10% return, a 25% chance of earning 20% and a 25% chance of earning -10%, the expected return would be equal to 7.5%:
= (0.5) (0.1) + (0.25) (0.2) + (0.25) (-0.1)
= 0.075
= 7.5%Although this is what you expect the return to be, there is no guarantee that it will be the actual return.
expense charge
A monthly charge paid to an insurance company based on various characteristics of the insured, such as age. Charges are defined for a specified period of time as provided in the life insurance policy.
experience rating
The process of using a group´s own premium and claims experience to calculate premium rates. If the claims experience for the previous year was favorable, the insurer considers reducing the premium rates for the coming year. If the experience was unfavorable, the insurer attempts to discover the reason and may propose higher premium rates for the next year. See also blended rates and manual rates.

F . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
face amount
In a life insurance policy whose benefit is not variable, the amount stated as payable at the death of the insured or (in the case of an annuity) at the maturity of the contract. It is generally shown on the first page of the policy. Also called the face value. See also basic death benefit, death benefit, and policy proceeds.
family benefit
A life insurance policy rider that provides term insurance coverage on the insured´s spouse and children.
field offices
An insurance company´s local sales offices.
field underwriting
The first step in the risk selection process. Field underwriting occurs when an agent gathers pertinent information about the proposed insured and reports that information on the application blank so the home office underwriter can make an underwriting decision.
final expenses
Expenses that occur at the death of an individual that must be paid before concluding the probate process. Examples include estate taxes, medical bills, funeral expenses, legal fees, probate costs, outstanding debts, appraisal fees and the like.
first-year commission
An amount paid to an insurance agent based on a policy´s first annual premium amount.
fixed annuity
A fixed annuity is a financial product issued by an insurance company. It minimizes tax liability, while allowing tax-deferred growth of assets. At retirement, a fixed annuity can provide a guaranteed income stream, in specified amounts, for a specified period or for life.
flexible premium deferred annuity
An annuity that allows additional payments after the initial funding with annuitization beginning after a specified number of years.
fraudulent claim
A type of claim that occurs when a claimant intentionally uses false information in an attempt to collect policy proceeds.
fraudulent misrepresentation
According to common law, a false statement which meets the following three criteria: (1) the party that makes the statement is aware that it is not true or disregards whether it is true; (2) the party that makes the statement does so in order to induce another party to enter into a contract; (3) the other party does enter into a contract as a result of the statement and suffers a loss because of the contract.
free examination period
The period of time after delivery of an insurance policy during which the policyowner may review the policy and return it to the company for a full refund of the initial premium. Full coverage is in force during this period. Also called a ten-day free look or free-look provision.
fully contributory
An arrangement in which the insureds under a group policy pay the entire cost of their insurance. Contrast with contributory group insurance and noncontributory group insurance.
G . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
grace period
The length of time (usually 31 days) after a premium is due and unpaid during which the policy, including all riders, remains in force. If a premium is paid during the grace period, the premium is considered to have been paid on time.
group insurance
Insurance that provides coverage for several people under one contract, called a master contract.
group representative
A salaried insurance company employee who deals solely with the distribution of group insurance products. The primary responsibilities of group representatives include finding prospects, designing proposals, installing the product, and renegotiating the policy at renewal.
guaranteed insurability rider (GI)
An amendment to a life insurance policy that gives the policyowner the right to purchase additional insurance of the same type as provided in the original policy. The additional insurance can equal no more than an amount specified in the policy contract and can be purchased at specified premium rates and at specified times without new evidence of insurability. Also called a policy purchase rider.
guaranteed interest
Each policy or contract contains a minimum guaranteed interest rate. The current interest rate may be greater than or equal to the guaranteed interest rate. Interest earned over and above the guaranteed interest rate is the excess interest. The total amount of interest earned on a policy or contract is the sum of the guaranteed and excess interest amount.
guaranteed-issue insurance
Insurance coverage for which there is usually no individual underwriting. All eligible members of a particular group of proposed insureds who apply for the policy and who meet certain conditions are automatically issued a policy.
H . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
human life value
The value of the tasks a family member provides to the rest of the family. The economic value for a non-working spouse would be equal to the cost the family would incur to hire someone to complete the tasks in the absence of the non-working spouse less the cost of that spouse´s personal maintenance. These costs usually include childcare and housekeeping but may also include transportation, the cost of eating out more often, tutoring and the like.
I . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
illness perils
A classification used by health insurance underwriters to evaluate the type and degree of peril represented by a particular occupation. Illness perils include exposure to dust, poisons, and extreme temperatures. See also accident perils.
illustration
A proposal showing a policy´s future payments, cash value and death benefits. Non-guaranteed values are based on the company´s current rates of interest, mortality and expenses.
immediate annuity
This allows you to convert a lump sum of money into an annuity so that you can immediately receive income. Payments generally start about a month after you purchase the annuity. This type of annuity offers financial security in the form of income payments for the rest of your life. In other words, you cannot outlive it. Also called Single Premium Immediate Annuities (SPIAs).
income protection insurance policy
A type of disability income policy which specifies that an insured is disabled if that person suffers an income loss caused by a disability.
income replacement ratio
The percentage of preretirement income that a retiree would need to receive after retirement in order to have a postretirement standard of living equivalent to his or her preretirement standard of living. This ratio is generally less than 100 percent, because some of an individual´s expenses (i.e., taxes, commuting costs, clothing expenditures, savings needs) decrease after retirement. Also known as the replacement ratio.
Life insurance policy clause that provides a time limit (usually two years) on the insurer´s right to dispute a policy´s validity based on material misstatements made in the application. See also contestable period.
individual insurance
Insurance that is issued to an individual person, as contrasted with group insurance. See also ordinary life insurance.
Individual Retirement Annuity (IRA)
An annuity, available as a retirement account, to someone who is employed. IRAs receive favorable tax status under Section 408 of the Internal Revenue Code. IRAs are sometimes referred to as Individual Retirement Accounts. There are 5 different types of IRAs. They are: the Traditional IRA, Education IRA, Roth IRA, Simple IRA, and SEP IRA - Simplified Employee Pension.
initial premium
The first premium payable for an insurance contract.
installation
The term used to include all the activities from the time a prospect decides to purchase a group insurance policy to the time the master contract and its individual certificates are issued.
insurability
Acceptability to the company of an applicant for insurance.
insurable interest
A condition in which the person applying for an insurance policy and the person who is to receive the policy benefit will suffer an emotional or financial loss if the event insured against occurs. Without the presence of insurable interest, an insurance contract is not formed for a lawful purpose and, thus, is void from the start.
insurance
A system of protection against loss in which a number of individuals agree to pay certain sums of money, called premiums, to create a pool of money which will guarantee that the individuals will be compensated for losses caused by events such as fire, accident, illness, or death.
insured / insured life
A person whose life is insured by an insurance policy.
insurer
The party in an insurance contract that promises to pay a benefit if a specified loss occurs. Usually an insurance company.
inter vivos
See living trust.
interest rate (current)
This is the current interest rate credited to the policy or contract.
interest rate (guaranteed)
The guaranteed minimum annual interest rate used in calculating items such as policy reserves from year to year. Also the guaranteed factor is used to calculate interest payable on proceeds held under a settlement option. This term also refers to the minimum rate credited each year to any cash values.
interest rate (loan)
The current rate at which interest is charged for a life insurance policy loan.
IRA
See Individual Retirement Annuity.
irrevocable beneficiary
A beneficiary in a life insurance policy or segregated fund contract whose compensation cannot be changed without his or her consent.
irrevocable trust
A trust usually established by an individual that may not be changed or revoked in the future. The individual setting up the trust is usually referred to as the grantor. The grantor surrenders control over the property by transferring it to the trust. Thereafter, the trust assets are controlled by the trustee of the trust who manages and distributes assets to the trust beneficiaries according to the terms spelled out in the trust document. Since the property that is transferred to the trust is no longer owned or controlled by the grantor, it does not pass through probate and is no longer subject to federal estate taxes. However, the transfer of property to an irrevocable trust may cause gift tax liability. Before you transfer property to an irrevocable trust, you should ensure that you understand the full ramifications of your action by consulting your tax advisor.
issue age
The insured´s age at the time coverage takes effect. Insurance plans typically define issue age as the age at the insured´s last birthday or the insured´s nearest birthday.
issue date
The effective date of the policy or contract as issued by the insurer.

J . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
Annuity that makes payments for the lifetime of two or more beneficiaries, often a husband and wife. When one of the annuitants dies, payments continue to the survivor annuitant in the same amount or in a reduced amount as specified in the contract. Also called joint life annuity or survivor annuity.
joint life annuity
See joint annuity.
joint beneficiaries
Parties that share in any death benefits payable under the life insurance policy or annuity contract. If no beneficiary has been named on the policy, the benefits usually pass directly to the estate of the deceased owner, and thereby fail to avoid probate.
K . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
key-person insurance
Life insurance purchased by a business on the life of a person (usually an employee) whose continued participation in the business is necessary to the firm´s success and whose death or disability would cause financial loss to the company.
L . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
lapse
The termination of an insurance policy because premiums were not paid when they came due.
law of large numbers
The theory of probability which specifies that the greater the number of observations made of a particular event, the more likely it will be that the observed results will approximate the results anticipated by the mathematics of probability.
level commission schedule
A commission schedule that provides the same commission rate for the first and renewal years.
level premium life insurance
Life insurance for which the premium remains the same from year to year. The premium is normally more than the actual cost of protection during the earlier years of the policy and less than the actual cost in the later years. The building of a cash value is a natural result of level premiums over a long period. Term policies generally have level premiums for the initial term, though they generally have no cash value. The payments in the early years, together with the interest that is to be earned, serves to balance out the underpayment of the later years.
liability
A financial obligation, debt or claim against a person or institution.
licensed insurance agent
Agents must be licensed by the state(s) where they sell insurance products. Many are trained to assist you in determining your insurance needs for life, health, disability, insurance as well as annuity contracts. Also see Broker.
life insurance
Insurance that provides protection against the economic loss caused by the death of the person insured.
life annuity
A life annuity is a fund that you contribute to during your working years, while you have a steady and reliable income. The advantage to investing in a life annuity, instead of just saving the money yourself, is two-fold: your investment grows according to the interest rates the life annuity offers, and the money is tax-free until it is withdrawn from the life annuity. The funds in a life annuity will not be taxed until you retire and start receiving payouts, at which time it is considered income and is taxed as such.
life expectancy
The average number of years a person is expected to live. Life expectancy is projected from a mortality table and is used to calculate benefit payouts.
lifetime income with period certain
The lifetime option provides payments for as long as you live for a Period Certain or Refund options, which provide payments for the longer of your life or some fixed period (generally 5, 10, 15, or 20 years). If you die before the period ends, your beneficiaries receive the remaining payments or a cash refund.
limited-pay life
A whole life insurance policy where the premiums are paid for a limited period of time such as 20 years or until age 65 rather than for the life of the insured. At the end of the payment period, the policy becomes "paid-up" and guarantees death benefit protection in the face amount for the remainder of the insured´s life without further premiums.
LIMRA
Life Insurance and Market Research Association (now LIMRA International, Inc.)
liquidity
The ability of an asset to be converted into cash quickly and without significant loss of value.
A trust established during the lifetime of the person creating the trust, rather than under the person´s will. Also known as an inter vivos trust.
loading
A charge that the insurer adds to the net premium to produce the gross premium actually paid by the policyowner. The loading is designed to cover the operating expenses of the company, to compensate the company for the loss of income when policies lapse and to provide margins for profits and contributions to surplus.
A loan made by a life insurance company from its general funds to a policyowner on the security of the cash value of a policy. Generally, loans reduce the policy´s death benefit and cash value by the amount of the outstanding loan plus interest. Also known as a loan provision.
loan provision
See loan.
long-term disability income insurance
Disability income insurance which typically provides disability income benefits that begin at the end of a specified waiting period and that continue until the earlier of the date when the insured person returns to work, dies, or becomes eligible for pension benefits. See also disability income insurance and short-term disability income insurance.
loss ratio
In pricing health insurance, the loss ratio is a means of comparing claims losses to premium earnings. To determine its loss ratio, an insurer divides the dollar amount of claims it incurred during a given year by the dollar amount of premiums it earned during the same year.
M . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
manual rates
Premium rates that are established for broad classes of groups. Manual rates are often used to establish premium rates for small groups with no credible loss experience, and to establish initial premium rates for large groups. See also blended rates and experience rating.
master contract
The legal contract between an insurance company and a group insurance policyholder. The master contract insures a number of people under a single contract. Also called the master policy. See also certificate of insurance.
material misrepresentation
In insurance, a misstatement by an applicant that is relevant to the insurer´s acceptance of the risk, because, if the truth had been known, the insurer would not have issued the policy or would have issued the policy on a different basis.
maturity date
The maturity date is the end of the contract term.
maximum benefit period
The maximum length of time for which disability income payments will continue.
maximum loan amount
The maximum amount of money a policy owner can borrow using the cash value of the life insurance policy as security.
medical application
An application for insurance in which the proposed insured is required to undergo some type of medical examination. The results of the medical examination are then reported to the insurance company.
Medical Information Bureau (MIB)
MIB is organized as a non-stock, not-for-profit membership association of life insurance companies. MIB conducts a confidential interchange of information of underwriting significance among its member life insurance companies. The interchange enables MIB member companies to protect the interests of prospective insurance consumers, policyholders and life insurance companies from consumers who omit or misrepresent material facts on their applications for life, health or disability insurance. If in the underwriting of an application for insurance, an MIB member company develops information which is significant to health or longevity, a brief, coded resume of such information will be submitted to MIB. If the consumer applies to another MIB member insurance company, that company may request a copy of the report from MIB provided it has obtained from the consumer a written authorization naming MIB as an informational source. Under the general rules of the association, an insurance company may not base its underwriting decision solely on information provided by MIB. Each member company must conduct its own underwriting investigation. Access to MIB information is restricted to each member company´s authorized medical, underwriting and claims personnel. Consumers may request disclosure of or correction to their MIB record by contacting the MIB Information Office, P.O. Box 105, Essex Station, Boston, MA 02112, (617) 426-3660.
medical report
A report on a proposed insured´s health that is completed by a physician and is based on a physical examination and questioning of the proposed insured. Such a medical report serves as part of a medical application.
MIB
See Medical Information Bureau.
minimum rate guarantee
The minimum fixed interest rate an insurance company pays on the cash value of a whole life or universal life insurance policy. The minimum rate guaranteed is stated in the insurance policy.
misrepresentation
- A false or misleading statement made to induce a prospect to purchase insurance. Misrepresentation is a prohibited insurance sales practice.
- A false or misleading statement made by an applicant for insurance. Certain misrepresentations provide a basis for the insurer to avoid the policy.
misstatement of age provision
Life insurance policy wording that specifies the action the insurer will take if, at the insured´s death, the insurer discovers that the insured´s age was misstated in the application and the misstatement has resulted in an incorrect premium for the amount of insurance purchased. In an individual life insurance policy, this provision specifies that the policy´s benefit amount will be adjusted. In a group insurance policy, this provision generally specifies that the policy´s premium amount will be adjusted.
mode of premium payment
The frequency with which premiums are paid (for example, annually, quarterly, monthly).
monthly anniversary
The same day as the policy date for each succeeding month.
monthly point to point crediting method
This crediting method takes the starting point of each policy month and compares it to the ending point of the policy each month, disregarding fluctuations in between. Each month has an index result that can be positive or negative. At the end of the contract year, the monthly results are added together. If the end result is positive, then interest is credited to the contract. If negative, then the contract will not earn any interest.
morbidity
Sickness, disability, or failure of health.
morbidity rate
The likelihood that a person of a given age will suffer an illness or disability. The premium that a person pays for health insurance is based in part on the morbidity rate for that person´s age group.
morbidity table
A chart that shows the rates of sickness and injury occurring among given groups of people categorized by age.
mortality charge
The cost of the insurance protection on a whole life product. On an illustration, mortality charges referred to as "current" are not guaranteed. Those stated as "maximum" are the contract guarantees. The mortality charge is similar to a one-year term rate and increases with the insured´s attained age. For example, a typical $100,000 whole life policy for a 40-year-old male carries a premium of about $2,000 a year. Of that, roughly $350 is the mortality charge, and the rest of the premium goes toward the investment portion.
mortality table (SSA Period Life Table)
An actuarial table indicating life expectancy and probability of death as a function or age and sex and occupation etc.
mutual benefit method
An early method of funding life insurance, formerly used by fraternal orders or guilds. Under the mutual benefit method, the promised death benefit was provided by charging participating members an equal amount after the death of an insured member. Also called the post-death assessment method. See also assessment method.
mutual fund
An investment account that invests in a variety of securities selected according the fund´s objective. Managed by a professional portfolio manager, a mutual fund may invest in any combination of cash equivalents, stocks, or bonds. Rather than having a single investor, mutual funds pool the money of many investors each of whom owns a proportionate share of the fund. Each investor shares in the fund´s income or capital gains or losses in proportion to the investor´s ownership interest.
Apply Online for Dental & Vision Coverage
N . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
net amount at risk
The net amount at risk is the difference between the limit of insurance or face amount of the policy and the reserve or cash value that has accumulated.
net cash surrender value
The cash surrender value less any outstanding loans and/or surrender charges.
net worth
Total assets minus total liabilities of an individual or company.
new business department
no-evidence limit
In group insurance, the maximum amount for which an insurance company will insure an individual without first securing evidence of insurability. Also known as the guaranteed issue limit.
noncontributory group insurance
A group insurance plan in which the insureds pay no portion of the premium for their insurance. The group policyholder pays the entire premium. If a group plan is noncontributory, the enrollment of group members is automatic; all eligible group members are covered. Contrast to contributory group insurance.
noncontributory plan
A pension or employee-benefit plan in which contributions are made entirely by the plan sponsor. Contrast with contributory plan.
nonforfeiture values
A benefit to a life insurance policyholder that provides the amount of money (cash surrender value), the amount of extended term insurance, or the amount of paid-up insurance available from a life insurance policy to its owner when terminated by that person before the policy matures.
nonmedical application
An application for insurance in which the proposed insured is not required to undergo a medical examination. However, a nonmedical application does contain questions that the proposed insured must answer about his or her health. See also nonmedical supplement.
nonmedical supplement
A report that describes the proposed insured´s health history. A nonmedical supplement is completed by the agent based on information provided by the proposed insured and can serve as part of a nonmedical application. Also called a nonmedical declaration. See also nonmedical application.
nonparticipating policy
A type of life insurance policy or annuity in which the policyowner does not receive policy dividends. Also called a nonpar policy.
nonsmoker risk class
An underwriting risk class that includes people who are standard risks and who have not smoked cigarettes for a specified period of time, usually 12 months, before applying for insurance. People in the nonsmoker risk class pay lower than standard premiums.
O . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
occupation class
A group of occupations that present a similar risk to an insurance company. If all other factors are equal, people in the same occupation class will pay the same premium rates for health insurance.
ordinary life
A whole life insurance policy where the premiums are paid throughout the life of the insured. Also known as "straight life".
An optional policy rider that provides convertible term insurance to a spouse or an immediate family member of the primary insured. You will be charged an additional premium.
overinsurance
An amount of insurance that is excessive in relation to the loss insured against.
owner
See policyowner.
P . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
paid-up additions
The cash value of dividends earned that were used to purchase paid-up additional insurance.
paid-up policy
Insurance that will remain in force with no need to pay additional premiums.
paramedical report
A report based on a physical examination and a medical history completed by a medical technician, a physician´s assistant, or a nurse, rather than a physician. A paramedical report describes the health of a proposed insured and can serve as part of an insurance application.
partial disability
A disability that prevents an insured from engaging in some of the duties of his or her usual occupation or from engaging in the occupation on a full-time basis.
A flat amount specified in a disability income insurance policy that is payable when the insured suffers a partial disability. Usually the partial disability benefit is half the full disability benefit. See also residual disability benefit.
participating policy
A type of life insurance policy or annuity under which policy dividends may be paid to the policyowner. Also called a par policy. See also dividend.
payee
The person named to receive annuity payments from an annuity contract.
payor
The person making premium payments on a policy or contract. If the payor is not also the owner, they may not be entitled to exercise the rights and provisions of the policy or contract.
payroll deduction plan
A premium payment method for individual insurance under which an individual´s employer deducts the employee´s premium amount from his or her paycheck and sends the premium to the insurer. See salary-reduction plan.
percentage contribution
The amount of the premium that a group member pays in a contributory group insurance plan. Also known as employee contribution or member contribution. See also contributory group insurance.
period-certain annuity
An annuity that provides guaranteed payments to an annuitant for a specified period of time.
permanent and total disability
A condition that prevents an insured from returning to any gainful employment.
permanent life insurance
Any form of life insurance except term; generally insurance that builds up a cash value, such as whole life. Coverage can last a lifetime.
persistency
The retention of business that occurs when a policy remains in force as a result of the continued payment of the policy´s renewal premiums.
personal interview report
A report that contains the same types of information as an inspection report, except that the personal interview report relies on the proposed insured as the only source of information. See also inspection report.
plan participant
A person on whose behalf contributions are made or benefits are accrued under a pension or employee-benefit plan.
plan sponsor
An entity which has adopted and maintains a pension or employee-benefit plan. The plan sponsor is often an employer, but may be a union, a trade or professional association, or a committee composed of representatives of a number of employers or associations.
planned periodic payment
The premium designated at the time of the application as the amount planned to be paid at specific intervals until the maturity date.
POA
point-to-point indexing method
The index-linked interest, if any, is based on the difference between the index value at the end of the term and the index value at the start of the term. Interest is added to the annuity at the end of the term.
A written document that serves as evidence of an insurance contract and contains the pertinent facts about the policyowner, the insurance coverage, the insured, and the insurer.
policy anniversary (policy date)
The anniversary of the date on which a policy was issued. Sometimes simply called the anniversary.
policy charge
An amount that an insurer adds to the gross premium to help cover the insurer´s expenses. This amount is the same regardless of the size of the policy. Also called a policy fee.
policy loan
See loan.
policy value
A universal life insurance policy´s equivalent of a cash value. The policy value is built by the accumulation of premiums plus interest less charges for expenses and mortality costs and other risk charges. In variable policies, this accumulation depends on the performance of the underlying assets and not on an interest rate set by the insurance company.
policyholder
The person who owns a life insurance policy. This is usually the insured person, but it may also be a relative of the insured, a partnership or a corporation.
The person or party who owns an individual insurance policy. The policyowner is not necessarily the person whose life is insured. The terms policyowner and policyholder are frequently used interchangeably.
policy proceeds
The amount that the beneficiary actually receives from a life insurance policy after adjustments have been made to the basic death benefit for policy loans, dividends, paid-up additions, late premium payments, and supplementary benefit riders. Compare to basic death benefit and death benefit. Also called net policy proceeds.
policy provisions
The statements, following the face page of an insurance policy, that describe the operation of the insurance contract.
An amount set aside by an insurer specifically to fulfill the obligations of a policy. While such reserves may be calculated as an aggregate amount, covering many policies, it is assumed that each policy has a pro rata share of the total reserve. This reserve is for the increased claim rate encountered as the policyholder population ages.
policy year
The 12-month period between a policy´s anniversaries.
pooling
In group insurance, the practice of underwriting a number of small groups as one large group.
portability
The ability of an individual to transfer from one health insurer to another health insurer without regard to preexisting conditions or other risk factors.
Authority given to a person to act in one´s behalf on most required activities.
preexisting condition
A health problem that existed before the date your insurance became effective. Many insurance plans will not cover preexisting conditions. Some will cover them only after a waiting period.
preexisting conditions provision
A provision in most medical expense insurance policies stating that until the insured has been covered under the policy for a certain period, the insurer will not pay benefits for any preexisting condition.
preferred risk class
In life insurance, a risk class that consists of individuals whose anticipated mortality is lower than the norm established for the standard risk class. Among other things, people in the preferred risk class are in excellent physical condition, have good family medical histories, and do not smoke. Sometimes called the superstandard risk class.
premium
Payments to the insurance company to buy a policy and to keep it in force.
premium mode
Frequency of premium payment, monthly, quarterly, or annually as selected by the policy owner.
presumptive disability
A condition that, if present, automatically causes an insured to be considered totally disabled. Examples of presumptive disabilities are total and permanent blindness or loss of two limbs.
primary beneficiary
The party or parties who have first rights to receive policy benefits when the benefits of an insurance policy become payable.
An optional policy rider that provides level term insurance on the primary insured. When the primary insured rider is combined with the base coverage, it can reduce premium costs for the amount of coverage as compared to the cost of permanent plan of the same face amount.
probability
The likelihood of some event occurring. In mathematics, probability is the number of times that something is likely to occur out of a number of possible occurrences. Probability theory is an essential aspect of the mathematical foundations of insurance.
probate
The judicial process of proving the validity of a will under state law. The goal of these laws is to ensure that the decedent´s estate is settled correctly and that those entitled to the decedent´s property both under the will and under state law receive that property.
probationary period
See waiting period.
proximate cause of death
An event that is directly responsible for a death or an event that initiates an unbroken chain of events that lead to death.
Q . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
qualified plan
In the United States, a pension plan or employee-benefit plan which meets a series of federal government requirements and is therefore eligible for certain tax advantages.
R . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
rate making
The calculation of premium rates for an insurance company´s products. Actuaries consider several factors when they establish life insurance premium rates. The most important factors are mortality rates, interest rates, and loading.
rated
An insurance company reviews information about you, such as the state of your health, your financial situation, and, if necessary, whether your job and hobbies impact your risk profile. An applicant will typically apply for the most favorable risk class available, and over 80% of the time we will be able to offer a policy in that class after the risk appraisal is completed. Sometimes, however, an additional premium (rating) may be needed to cover an aspect of your risk profile that makes you a less favorable risk. The amount of the additional premium will vary with the degree of extra risk involved, and can also vary by insurance plan.
rating classes
The three different approaches that insurers take when they use mortality assumptions to calculate group life insurance premiums. The three rating classes for group premiums are manually rated premiums, experience rated premiums, and blended premiums. See also blended rates, experience rating, and manual rates.
recovery benefit
A partial or residual disability benefit payable after an insured satisfies a qualification or an elimination period, returns to work, and then suffers a loss of earnings directly resulting from a preceding total or partial disability. Also known as income replacement benefit. See also partial disability benefit and residual disability benefit.
reinstatement
The process by which a life insurance company puts back in force a policy that had lapsed because of nonpayment of renewal premiums.
reinstatement provision
A life insurance policy provision that describes the conditions the policyowner must meet in order for the insurer to reinstate the policy if it has terminated because of nonpayment of renewal premiums.
reinsurance
A transaction between two insurance companies in which one company purchases insurance from the other to cover part or all of the risks that the first company does not wish to retain in full. See also ceding company and reinsurer.
reinsurance treaty
A broadly worded statement of the agreement between a reinsurer and a ceding company. The three common types of reinsurance treaties are automatic, facultative, and facultative-obligatory. Usually just called a treaty. See also automatic reinsurance treaty, facultative reinsurance treaty, and facultative-obligatory (fac-ob) reinsurance treaty.
reinsurer
An insurance company that accepts the risk transferred from another insurance company in a reinsurance transaction. Also called the assuming company.
relation of earnings to insurance clause
A clause included in some guaranteed renewable or noncancellable individual disability policies that limits the amount of benefits in which an insurer will participate when the total amount of disability benefits from all insurers exceeds an insured´s usual earnings. Also known as a participation limit.
renewable term insurance
Term insurance that can be renewed at the end of the term, at the option of the policyowner and without evidence of insurability, for a limited number of successive terms. The rates generally increase at each renewal as the age of the insured increases.
renewal commissions
Those commissions paid to the agent for a specified number of years, usually nine, after the first policy year. The renewal commission rate is generally much lower than the first-year commission rate and is paid only on policies that remain in force.
renewal premiums
Premiums payable after the initial premium.
renewal provision
- An individual life insurance policy provision that gives the policyowner the right to continue the insurance coverage at the end of the specified term without submitting evidence of continued insurability.
- A provision in an individual health insurance policy describing the circumstances under which the insurance company may refuse to renew the coverage, may cancel the coverage, or may increase the policy´s premium rate.
replacement
The act of surrendering an insurance policy or part of the coverage of an insurance policy in order to buy another policy.
representation
A statement by an insurance applicant of facts upon which the insurer bases its decision as to whether or not to issue the policy as applied for.
rescission
An equitable remedy under which the insurer seeks to void a policy or have it declared void. Rescissions usually occur when there has been material misrepresentation in the insurance application.
reserve
Typically, the liability account that identifies the amount of assets needed to pay future claims. There are many different types of reserves. When the term "reserve" is used in the life insurance industry, it usually refers to the policy reserve. See policy reserve.
reserve strengthening
The process of setting up additional policy reserves.
A partial disability benefit amount that is established according to a formula specified in a disability income insurance policy. The amount of the benefit varies according to the percentage of income loss attributable to the disability. See also partial disability benefit.
result clause
A type of war hazard exclusion that excludes payment of benefits only for losses resulting from war or acts of war.
retention
In reinsurance, the amount of a reinsured risk which the ceding company retains. See retention charge.
For a group insurance contract, the portion of the premium that is intended to cover expenses (other than claims) and to allow the insurance company to make a profit. Sometimes simply called retention.
retention limit
The maximum amount of insurance that an insurance company will carry at its own risk on any individual without ceding part of the risk to a reinsurer.
retroactive disability benefit
A type of disability benefit that is payable from the date of disability. The first payment is not made, however, until an elimination period has been satisfied.
return of premium
This type of life insurance is essentially a hybrid between term life and whole life. You buy a return of premium policy for a set amount of time — say, 30 years. You make your payments every year, and in the event that you pass away, your heirs are paid the face value of your death benefit. Here´s the part that appeals to a lot of people. Should you outlive your policy, the insurer sends you a tax-free check for the full amount that you´ve spent on premiums over the lifetime of your coverage. There is a downside. Price. In order to guarantee you your premiums at the end of the 30 years, the insurer charges you an additional 50% over the cost of a standard term policy.
revocable trust
A trust that may be altered or terminated during the grantor´s lifetime. Since the trust may be altered at any time until the grantor´s death, it is considered part of the grantor´s estate and is subject to taxation. The property is passed on to the beneficiaries only after the grantor´s death, and the revocable trust then becomes irrevocable.
An amendment to an insurance policy that becomes a part of the insurance contract and expands or limits the benefits payable. Also called an endorsement.
- accelerated death benefit
- accidental death benefit
- automatic increase rider
- children´s term rider
- guaranteed insurability option
- other insured rider
- primary insured rider
- waiver of monthly deduction
- waiver of premium
risk class
A group of insureds who present a substantially similar risk to the insurance company. Among the most common risk classes used by life insurance companies are standard, preferred, nonsmoker, substandard, and uninsurable.
risk tolerance
An investor´s ability to withstand declines in the value of his/her portfolio, financially and emotionally.
Rule of 72

S . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
salary continuation plan
A disability or sick-leave plan which provides for employees to continue to receive up to 100 percent of their salary for a limited number of days if they become ill or disabled. The number of days per year granted to an employee generally increases as the employee´s length of service increases. Most such plans are self-insured. Also known as a sick-leave plan.
A salary reduction plan is an agreement between you and your employer to reduce your salary by a given amount, based on the assumption that you´re going to use that money sometime during the year to pay for specific types of expenses. In effect, your employer sets up an account for you from which you can get reimbursed tax free.
A type of life insurance policy that insures two lives. The death benefit is payable at the second death. Generally, this product is used as a funding vehicle for estate taxes payable at the second death when the unlimited marital deduction is utilized. Also referred to as survivorship policies.
selection of risks
See underwriting.
self-administered group insurance plan
Under this type of group insurance plan, the group policyholder rather than the insurer performs most of the administrative work for the plan. The policyholder maintains detailed records of group membership, processes routine requests, such as requests for beneficiary changes and name and address changes, prepares its own premium statements, and, in some cases, prepares certificates for new group members.
self-insured group insurance
A form of group insurance in which the group sponsor, not an insurance company, is financially responsible for paying claims made by group insureds. A group may be partially or fully self-insured. See also administrative services only (ASO) contract.
short-term disability income insurance
Disability income insurance which provides a benefit for a short disability or for the first part of a long disability. See also disability income insurance, long-term disability income insurance, and weekly indemnity plan.
Single Premium Deferred Annuity (SPDA)
A single-premium deferred annuity lets you establish a stream of guaranteed retirement income with just one lump-sum payment. In addition, your cash value grows on a tax-deferred basis.
Single Premium Immediate Annuities (SPIAs)
Single Premium Immediate Annuities (SPIAs) are purchased with a single deposit amount. As the name implies, the annuity usually start making regular monthly payments to you immediately after you turn over the funds to the insurance company. Typically this means 30 days from the date of deposit; but within certain limits you can also to defer the date that payments begin.
single premium life insurance
Requires one lump-sum, up-front premium and is often guaranteed to remain paid-up throughout the insured´s lifetime.
small group insurance plan
A type of group life insurance plan that uses group underwriting techniques but adds some degree of simplified individual underwriting and is designed to cover groups containing 2 to 50 people.
Social Security
A program of the United States federal government that provides retirement income, health care for the aged, and disability coverage for eligible workers and their dependents.
Social Security Disability Income (SSDI)
A long-term disability income program that provides benefits to disabled workers who are under age 65 and who have paid a specified amount of Social Security tax for a prescribed number of quarter-year periods.
SPD
spouse and children´s insurance rider
An addition to a life insurance policy that provides coverage for a spouse and/or children.
SSDI
See Social Security Disability Income.
standard risk class
A risk class made up of individuals whose anticipated likelihood of loss is regarded as average. People in the standard risk class pay standard premium rates. Most insureds are included in the standard risk class.
suicide clause (provision)
Life insurance policy wording which specifies that the proceeds of the policy will not be paid if the insured takes his or her own life within a specified period of time (usually two years) after the policy´s date of issue.
Summary Plan Description (SPD)
- A document required by ERISA to provide information about a pension plan to plan participants in simple language. The SPD must, among other requirements, identify the plan´s administrator and those who are responsible for managing the plan´s assets, must explain the plan´s eligibility requirements and the circumstances under which a plan participant could forfeit his or her benefits under the plan, and must explain the procedures for making claims under the plan.
- A description of various aspects of a group insurance plan which must be provided to all plan participants and to the Department of Labor.
supplemental group life insurance
Life insurance over and above the basic coverage provided by a group policy. The supplemental coverage may provide an additional amount of the same type of insurance or may provide a different type of insurance. Supplemental coverage is usually contributory and subject to stricter underwriting standards than is the basic group coverage.
supplementary benefit rider
A rider that is added to an insurance policy to provide additional benefits. Some typical supplementary benefit riders are accidental death coverage, waiver of premium, and the guaranteed insurance option. See also rider.
surrender
The policy owner´s right to terminate policy coverage in exchange for the policy´s cash surrender value or other equivalent nonforfeiture values.
surrender charge
The fee an insurance company would assess against the cash value of a life insurance policy if the owner were to surrender the policy and during the surrender charge period. The amount of the surrender charge may be highest in the first few years and decrease over time until eventually it is zero.
surrender charge period
The number of years during which the insurance company would charge the owner a fee if the owner chooses to surrender the life insurance policy or annuity contract.
surrender charge schedule
A schedule showing the fee the insurance company charges for making early withdraws from the annuity contract.
survivors
Individuals, usually family members, who face emotional and sometimes financial setbacks because of your death.
survivor annuity
See joint annuity.
survivorship policies
See second-to-die.
T . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
temporary insurance agreements
Legal agreements between an insurer and a proposed insured that provide a guaranteed amount of temporary life insurance coverage for a specific period of time, usually the underwriting period. Also known as interim insurance agreements and temporary insurance receipts.
term insurance
term life insurance (Click here for a quote).
Life insurance that does not build up cash value and where the premium normally increases as the insured gets older. It always costs much less than whole life policies for everyone except the very advanced in age. There are two types of premiums: level term and annual renewable. Level-term premiums remain constant throughout the life of the policy and can be bought in increments up to 30 years, while premiums for annual renewable increase as you age. Ordinarily, level premiums are higher than renewable premiums in the early years of the policy and lower in the later years. These days the best bargains are to be found in level-term policies of 10 years and more.
third-party administrator (TPA)
An organization that administers an insurance contract for a self-insured group but that does not have financial responsibility for paying claims. The self-insured group pays its own claims. See also administrative services only (ASO) contract and self-insured group insurance.
top-heavy plan
In the United States, a pension plan or employee-benefit plan which provides more than 60% of its accrued benefits to the owners, executives or most highly paid employees of a company (known as key employees). To remain qualified, a top-heavy plan must provide certain minimum benefits to nonkey employee participants. See also key employee.
total collected
The total amount of all premium payments applied to the policy, less any payments reversed.
total disability
When a disability begins, it is typically considered a "total disability" if it prevents an insured person from performing the essential duties of his or her regular occupation. Under many insurance policies, the definition of total disability changes at the end of a specified period after the disability begins, usually two years. Therefore, insureds are considered totally disabled only if their disabilities prevent them from working at any occupation for which they are reasonably fitted by education, training, or experience. See also disability.
TPA
See third-party administrator.
travel accident benefit
An accidental death benefit often included in group insurance policies issued to employer-employee groups. This benefit is payable only if an accident occurs while an employee is traveling for the employer.
triple indemnity
A type of accidental death benefit coverage that pays an additional benefit equal to twice the policy´s basic death benefit if the accident is sustained while the insured is a passenger in a public conveyance operated by a licensed common carrier, such as a bus, train, or airplane.
trust
A legal arrangement that one party (the grantor or settlor) uses to transfer assets to a second party (the trustee). The assets are held and invested for the benefit of one or more third parties (the beneficiaries). See living trust and revocable trust.
trustee
The institution or individual that is named to hold, manage, and distribute a trust´s assets.
U . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
unclaimed benefits
Policy benefits for which no payee can be found. Under typical state statutes for unclaimed property, when an insurer cannot locate anyone entitled to policy benefits, the insurer will hold the unclaimed benefits for seven years and then turn them over to the state. Usually, the unclaimed property statute of the state of the beneficiary´s last known address applies. If no address is known, the statute of the insurer´s state of domicile will govern.
underwriter
- The person who assesses and classifies the potential degree of risk that a proposed insured represents.
- The person or organization that guarantees that money will be available to pay for losses that are insured against. In this sense, the insurance company is the underwriter.
- The process of assessing and classifying the potential degree of risk that a proposed insured represents. Also called selection of risks.
- Providing guarantees that money will be available to pay for losses that are insured against.
The department in a life and health insurance company that selects the risks that the company will insure. The underwriting department tries to make sure that the actual mortality or morbidity rates of the company´s insureds do not exceed the rates assumed when premium rates were calculated. The underwriter considers an applicant´s age, weight, physical condition, personal and family medical history, occupation, financial resources, and other selection factors to determine the degree of risk represented by the proposed insured. This department also participates in the negotiation and management of reinsurance agreements, through which an insurance company transfers some or all of an insurance risk to another insurance company. Also called the new business department.
underwriting manual
A summary of the methods used by a particular insurer to evaluate and rate risks. The underwriting manual provides underwriters with background information on underwriting impairments and serves as a guide to suggested underwriting actions when various impairments are present. See also risk class.
underwriting requirements
Printed instructions that indicate what evidence of insurability is required for a given situation and which of several optional information sources will be needed to provide underwriters with necessary information. Sources of information may include medical records and the results of physical examinations. Underwriting requirements are graduated based on the proposed insured´s age and the amount of coverage requested.
uninsurable risk class
The group of people with a risk of loss so great that an insurance company will not offer them insurance.
universal life insurance
A flexible premium life insurance policy under which the policyowner may change the death benefit from time to time (with satisfactory evidence of insurability for increases) and vary the amount or timing of premium payments. Premiums (less expense charges) are credited to a policy account from which mortality charges are deducted and to which interest is credited at rates, which may change from time to time.
V . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
variable life insurance
A permanent life insurance policy in which you direct how the policy value is invested by selecting from a variety of underlying portfolios (ranging in investment style and risk from conservative to aggressive) rather than earning a fixed rate of return.
void contract
A contract that is not valid. For example, a life insurance contract that lacks insurable interest is void for reasons of public policy.
W . . . . . . . . . . . . Back to the Top
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
- In medical expense insurance, a prescribed amount of time following policy issue during which the insured´s medical expenses are not covered by the policy. Such waiting periods usually last from 14 to 30 days following policy issue and normally apply only to medical expenses arising from sickness, not from accidents.
- In disability income insurance, a specified amount of time, beginning with the onset of the disability, during which benefits are not payable. Such waiting periods may last from seven days to six months. The waiting period in a disability income insurance policy is sometimes called the elimination period or the probationary period.
- In a group insurance plan, the length of time that a new group member must wait before being eligible to join the group plan. Also called a probationary period.
An optional life insurance policy rider that waives the monthly Cost of Insurance charges on a universal life policy for the length of a qualified disability as outlined in the policy contract.
A provision in an insurance policy that relieves the insured of paying the premiums while receiving benefits.
war exclusion provision
A life insurance policy provision that limits an insurer´s liability to pay a death benefit if the insured´s death is connected with war or military service. See result clause.
weekly indemnity plan
A type of short-term disability income insurance plan which typically pays a weekly benefit equal to a stated dollar amount or a percentage, such as 60 percent, of the insured person´s earnings.
will
A legally enforceable document allowing an individual to direct the distribution of his/her property after death.
withdrawal
Voluntary termination of an insurance contract by the policyowner. See also lapse.
whole life insurance
Policies that build cash value and cover a person for as long as he or she lives if premiums continue to be paid.

SIX REASONS YOU DON'T NEED LIFE INSURANCE
- You are never going to die.
- You are going to inherit a fortune.
- You are going to win the lottery.
- Your children are going to support you.
- The government will take care of you.
- You are never going to retire.
 Apply Online for Dental & Vision Coverage Apply Online for Dental & Vision Coverage
|
Barricks Insurance ServicesImportant Disclaimer: Answers and comments provided above are general information, and are not intended to substitute for informed professional medical, psychiatric, psychological, tax, legal, investment, accounting, governmental, or other professional advice. We do not endorse, and expressly disclaims liability for any product, manufacturer, distributor, service, health plan, or service provider mentioned or any opinion expressed in the website. Replies, comments, or information gathered on Barricks.com website may not be accurate but are intended to be helpful.